ArcGIS Pro, a GIS Geographic Information Systems the software used to create, store, and manage spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. , analyze spatial problems, and display the data in cartographic layouts Geographic Information Sciences software manufactured by a company called Esri out of Redlands, California, is probably the most popular and widely used GIS Geographic Information Systems the software used to create, store, and manage spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. , analyze spatial problems, and display the data in cartographic layouts Geographic Information Sciences software on the market. They became the most popular once they realized that analysts and technicians wanted to use vector and raster data Raster data is a type of digital data that stores information about a location using a grid of pixels or cells. All spatial rasters are raster files, but not all raster files are spatial rasters. within the same software at the same time. Once people saw a software that met their needs, it was on like Donkey Kong for Esri. ArcGIS Pro is the third major revision of GIS Geographic Information Systems the software used to create, store, and manage spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. , analyze spatial problems, and display the data in cartographic layouts Geographic Information Sciences software created by Esri and is different from the last incantation based mainly on the fact ArcGIS Pro is a multi-core software where ArcGIS Desktop (the previous major version) was a single-core software. As GIS Geographic Information Systems the software used to create, store, and manage spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. , analyze spatial problems, and display the data in cartographic layouts Geographic Information Sciences data became more complex and larger in size, ArcGIS Desktop just couldn't keep up. Esri decided to re-design a new product from the ground up with this in mind, along with the fact that computers have become more powerful are are capable of parallel processing of data (splitting the task into several pieces, each tacked by a separate core).
There are many parts of ArcGIS Pro, some of which deal with data organization (Catalog view/Catalog pane), one of which deals with 2D mapping (Map view), and two of which deal with 3D mapping (Local scenes and Global scenes). Additionally, there are sections that work with writing Python scripts for analysis and sections that allow for forms of data analysis automation (something we will have a chance to practice with in our final lab).
In GIS Geographic Information Systems the software used to create, store, and manage spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. , analyze spatial problems, and display the data in cartographic layouts Geographic Information Sciences 1040, you will be exposed mainly to two of those views - Catalog view and Map view. Catalog view can be described as the "File Explorer of spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. " where we organize and create blank copies of spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. (which are later populated with information utilizing Map view). Map view is what we use to interact with and explore our data, both spatially and in table form, and complete spatial analysis of that data (are you seeing the definition of GIS Geographic Information Systems the software used to create, store, and manage spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. , analyze spatial problems, and display the data in cartographic layouts Geographic Information Sciences software hiding in this paragraph?).
4.3.2: ArcGIS Pro Catalog View Overview
| Figure 4.3: ArcGIS Pro's Catalog View Basic Layout |
|---|
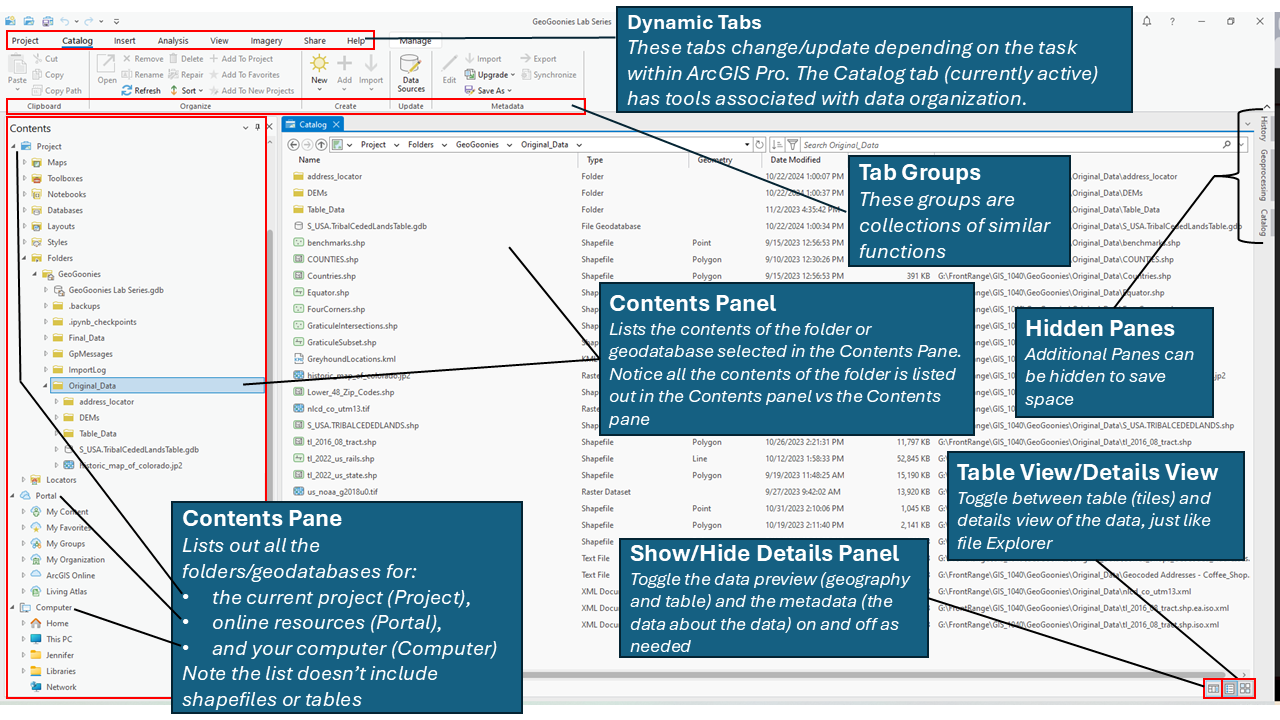 |
In Figure 4.3, we see a screenshot of ArcGIS Pro’s Catalog View, which replaces the standalone ArcCatalog application in previous versions of ArcGIS. We can identify it as Catalog View because the active tab at the top of the window is Catalog, and the main panel displays a folder’s contents in a structured layout. At the very top, we see the Dynamic Tabs, which change depending on the selected task within ArcGIS Pro. In this case, the Catalog Tab is active, providing tools related to data organization and management.
Below the dynamic tabs, we have the Ribbon, which contains tool Groups that organize similar functions. This ribbon-based interface replaces the traditional menu bar seen in older ArcGIS versions. Many of these groups contain options for importing, exporting, refreshing, and managing spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. . As we work with ArcGIS Pro in lab, these tools will become more familiar.
On the left side of the window, we see the Contents Pane, which lists all folders, databases, and connections available in the current project. Unlike the older Catalog Tree, the Contents Pane does not display shapefiles or tables directly—these are shown in the Catalog View when a folder or geodatabase electronic storage container specifically used to store geographic/ spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. with a top-down structure in which the items contained are related to each other and that relationship allows for the data to be quickly and efficiently queried and retrieved for use. is selected. In this example, the folder Original_Data is highlighted, meaning its contents appear in the main Catalog View Panel. The Table View/Details View toggle at the bottom right allows users to switch between a tabular list format and a more detailed view with metadata, similar to how File Explorer works.
To further customize the interface, Hidden Panes can be expanded or collapsed to maximize workspace, and the Show/Hide Details Panel button toggles additional metadata and preview information for selected files. The Catalog View provides a streamlined way to organize, search, and manage GIS Geographic Information Systems the software used to create, store, and manage spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. , analyze spatial problems, and display the data in cartographic layouts Geographic Information Sciences data efficiently, making it a crucial component of working in ArcGIS Pro.
The Details Panel
Metadata
Metadata is essential in GIS Geographic Information Systems the software used to create, store, and manage spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. , analyze spatial problems, and display the data in cartographic layouts Geographic Information Sciences because it provides detailed information about a dataset’s content, purpose, source, and structure. Just as a library book includes information about its author, publication date, and subject matter, metadata in GIS Geographic Information Systems the software used to create, store, and manage spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. , analyze spatial problems, and display the data in cartographic layouts Geographic Information Sciences documents key details about spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. . It allows users to understand what a dataset represents, where it came from, any limitations it may have, and how it should be used. Metadata ensures that GIS Geographic Information Systems the software used to create, store, and manage spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. , analyze spatial problems, and display the data in cartographic layouts Geographic Information Sciences professionals can properly interpret and share data across different projects and organizations.
In ArcGIS Pro, metadata follows a metadata standard format, which dictates the required fields and structure of the metadata. Different organizations and government agencies use standardized formats to maintain consistency when documenting GIS Geographic Information Systems the software used to create, store, and manage spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. , analyze spatial problems, and display the data in cartographic layouts Geographic Information Sciences data. Some commonly used metadata standards include:
- FGDC CSDGM (Federal Geographic Data Committee’s Content Standard for Digital Geospatial Metadata) – Used primarily in the U.S. federal government.
- ISO 19115 (International Organization for Standardization’s metadata standard) – A widely accepted global standard for geospatial metadata.
- INSPIRE (Infrastructure for Spatial Information in the European Community) – A European Union standard.
- Esri’s "Item Description" – The default metadata format in ArcGIS Pro, which includes essential fields such as title, description, extent, and tags.
The Details Panel in ArcGIS Pro allows users to quickly view an item's metadata. In Figure 4.4, the right side of the screen shows the metadata for the "COUNTIES.shp" shapefile One of the two main types of vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects we learn in this class (there are more than two vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects types in GIS). Shapefiles are each only one geometry type, either a point, a polyline, or a polygon. Shapefiles are stored in folders and most often do not have relationships with other data. , including information like tags, summary, extent, scale range, and citation details. Users can toggle the Show/Hide Details Panel button (bottom right corner) to display or hide metadata, making it easier to review key dataset details without opening a separate metadata editor. Understanding and maintaining metadata is a critical best practice in GIS Geographic Information Systems the software used to create, store, and manage spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. , analyze spatial problems, and display the data in cartographic layouts Geographic Information Sciences , ensuring that data remains well-documented, searchable, and reusable over time.
| Figure 4.4: Metadata Details in ArcGIS Pro Catalog View |
|---|
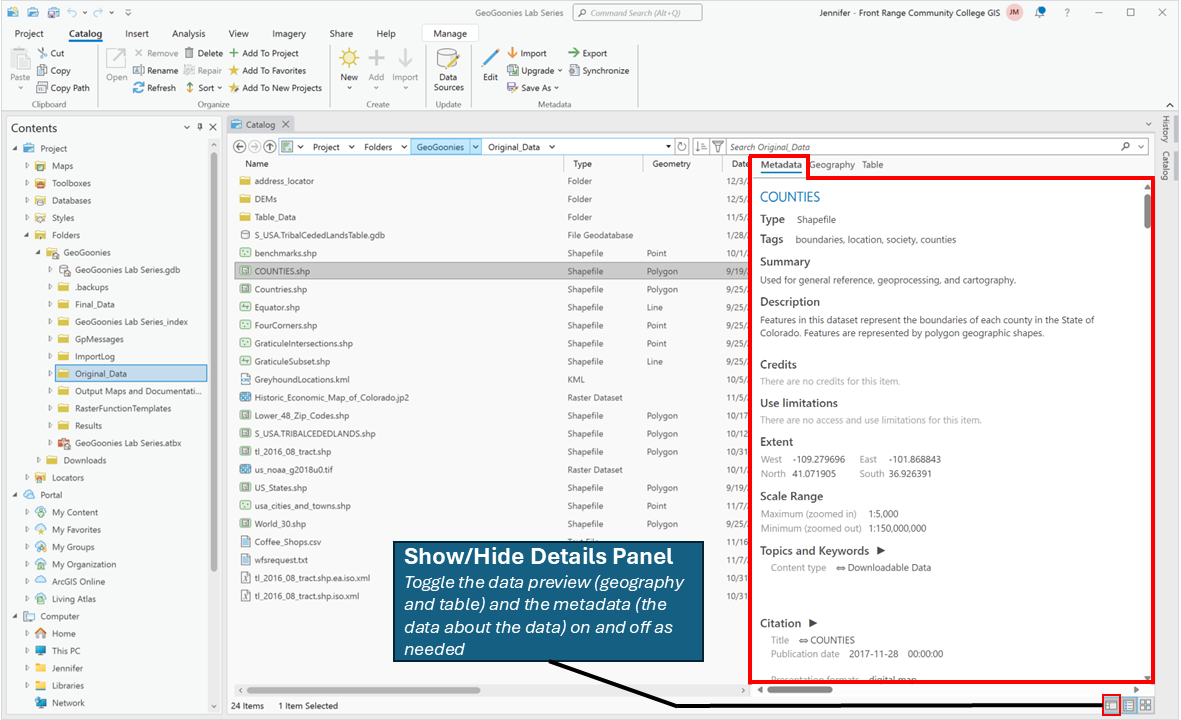 |
| The metadata details panel allows us to view the metadata of the selected item in various metadata standard formats. |
Preview Geography/Preview Table
ArcGIS Pro’s Catalog View allows users to quickly inspect spatial and tabular data without fully opening it in a map or table view. The Preview Geography and Preview Table options provide an efficient way to explore datasets before adding them to a project. These tools are especially useful when working with large datasets, unfamiliar data sources, or when verifying that a file contains the expected information before use.
The Preview Geography View allows users to visualize spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. directly within the Details Panel. When selecting a vector dataset, such as a shapefile One of the two main types of vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects we learn in this class (there are more than two vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects types in GIS). Shapefiles are each only one geometry type, either a point, a polyline, or a polygon. Shapefiles are stored in folders and most often do not have relationships with other data. or a feature class One of the two main types of vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects we learn in this class (there are more than two vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects types in GIS). Feature classes are each only one geometry type, either a point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. , a polyline A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of two or more vertices connected by straight lines. Often used to represent objects such as roads, river, and boundaries. , or a polygon. Feature classes are stored in geodatabases and are most often used when data relationships are important. within a geodatabase electronic storage container specifically used to store geographic/ spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. with a top-down structure in which the items contained are related to each other and that relationship allows for the data to be quickly and efficiently queried and retrieved for use. , the Preview Geography mode displays the dataset’s spatial features—points, lines, or polygons—on a simple, interactive map. Users can zoom, pan, and inspect the dataset’s structure without formally adding it to a project. This feature helps quickly determine whether a dataset contains the expected geographic features, check for missing data, or identify potential projection technically: the result of using one of variety of methods to transfer the geographic locations of features from a geographic coordinate system to a developable surface everyday use: any coordinate system, geographic or projected issues before loading it into a map.
| Figure 4.5: Geography Preview |
|---|
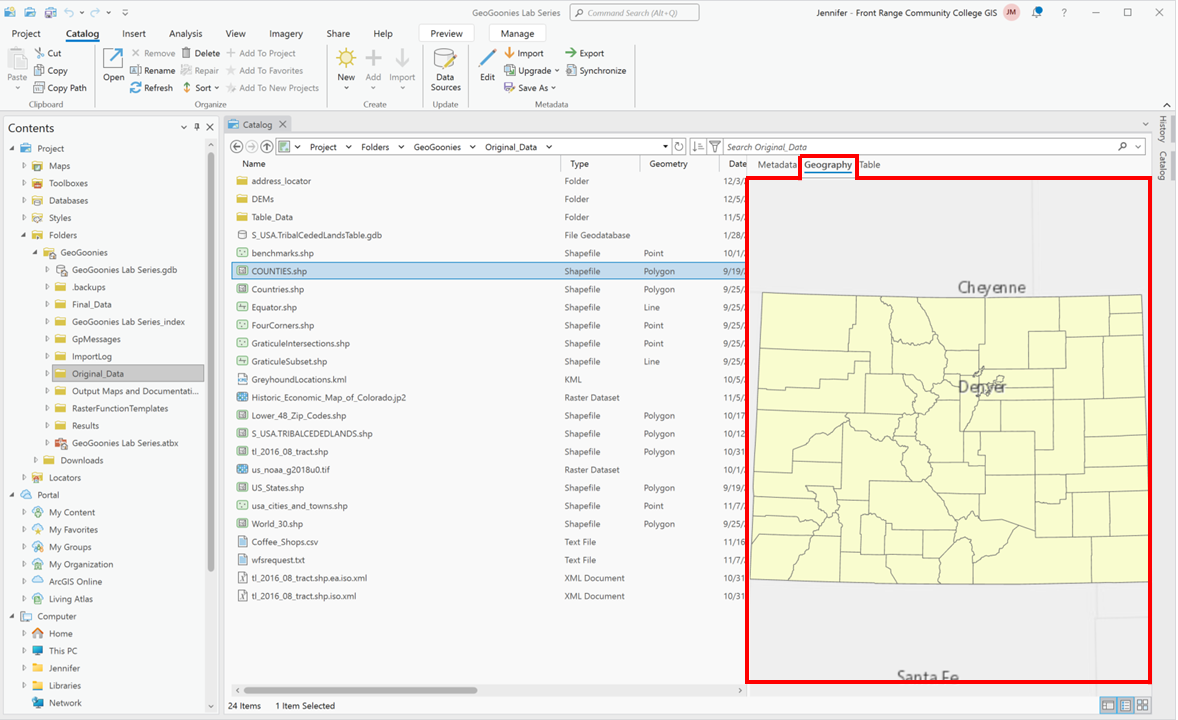 |
The Preview Table View, on the other hand, allows users to examine the attribute table of a selected dataset. When previewing a vector dataset, the table view displays all associated attributes, such as names, IDs, categories, or numeric values linked to each spatial feature. Similarly, for standalone data tables or integer raster datasets with attribute tables, this view reveals the structured information stored within. The ability to preview tables helps users check data integrity, confirm field names and values, and understand how attributes relate to spatial features—all without needing to open a separate attribute table window in the main interface.
| Figure 4.6: Table Preview |
|---|
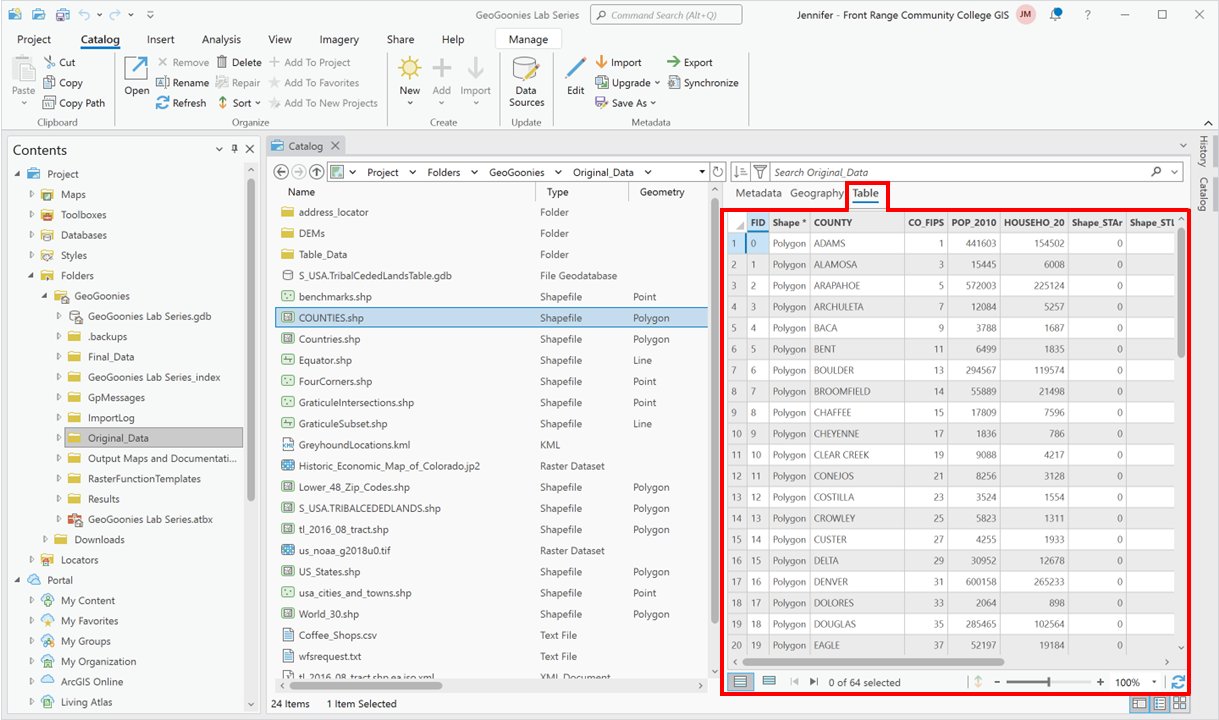 |
By using the Preview Geography and Preview Table Views, GIS Geographic Information Systems the software used to create, store, and manage spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. , analyze spatial problems, and display the data in cartographic layouts Geographic Information Sciences professionals can efficiently explore datasets and verify their contents, reducing errors and streamlining data selection. These preview tools ensure that only relevant and correctly structured data is added to a project, improving overall workflow efficiency in ArcGIS Pro.
Folder and Database Connections in ArcGIS Pro
In ArcGIS Pro, instead of manually granting "permission" to access folders as it was with ArcMap/ArcCatalog, we instead use folder connections and database electronic storage container with a top-down structure in which the items contained are related to each other and that relationship allows for the data to be quickly and efficiently queried and retrieved for use. connections within a project for convivence and organization. This approach streamlines workflow management by preventing users from having to navigate through all folders under "This PC" every time they need to access GIS Geographic Information Systems the software used to create, store, and manage spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. , analyze spatial problems, and display the data in cartographic layouts Geographic Information Sciences data. Folder connections allow users to quickly link commonly used directories, while database electronic storage container with a top-down structure in which the items contained are related to each other and that relationship allows for the data to be quickly and efficiently queried and retrieved for use. connections provide direct access to geodatabases without unnecessary navigation.
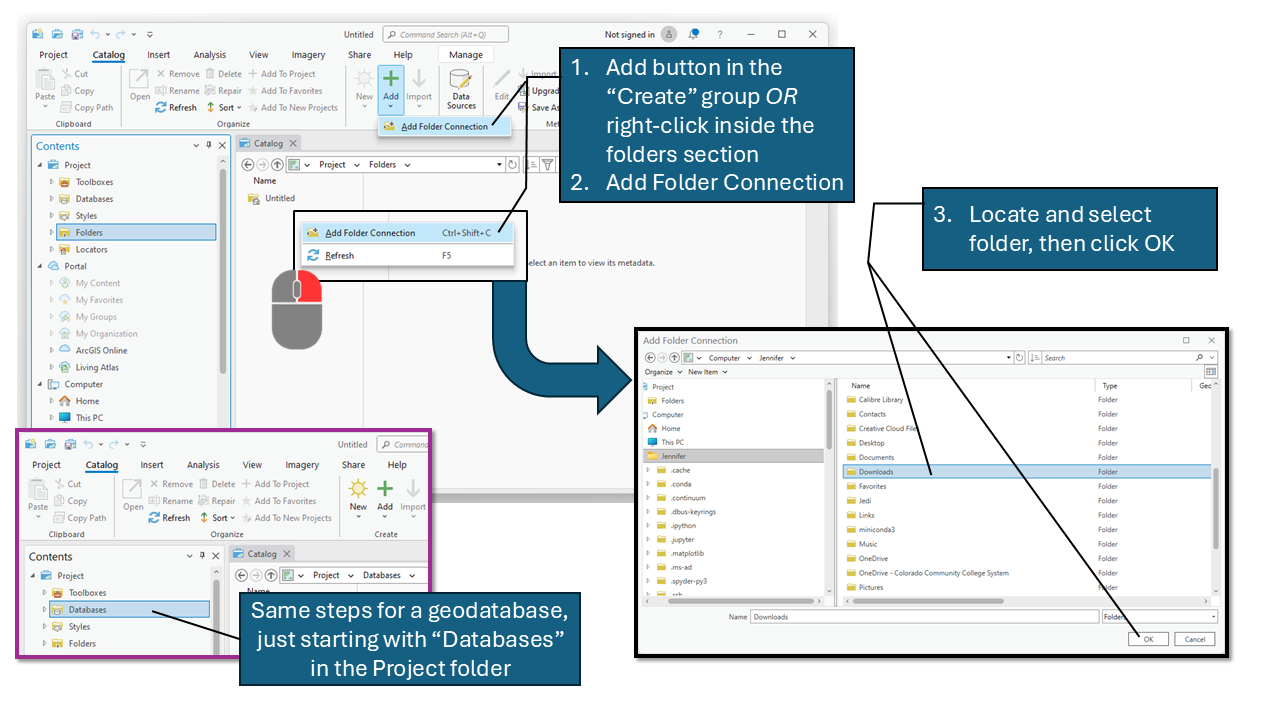
To add a folder connection, you can either:
- Click the Add Folder Connection button in the Create group under the Catalog tab.
- Right-click inside the Folders section of the Contents Pane and select Add Folder Connection.
- Browse to the desired folder, select it, and click OK.
This process automatically includes all subfolders, meaning if you connect to a higher-level directory, you gain access to everything within it without needing to add each subfolder individually. For this class, we will connect to the GIS Geographic Information Systems the software used to create, store, and manage spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. , analyze spatial problems, and display the data in cartographic layouts Geographic Information Sciences 1040 folder at the start, ensuring all necessary files are easily accessible throughout the semester. Since folder connections are saved within the project, you won’t need to reconnect every time unless you open a different project or switch machines.
Similarly, you can establish a database electronic storage container with a top-down structure in which the items contained are related to each other and that relationship allows for the data to be quickly and efficiently queried and retrieved for use. connection by navigating to the Databases section in the Contents Pane and following the same steps as adding a folder connection. This is particularly useful when working with geodatabases, as it allows direct interaction with feature classes, tables, and relationship classes without needing to browse file directories.
To remove a folder or database electronic storage container with a top-down structure in which the items contained are related to each other and that relationship allows for the data to be quickly and efficiently queried and retrieved for use. connection, simply right-click on its name in the Catalog Pane and select Remove. Unlike in ArcMap, this does not delete the folder or database electronic storage container with a top-down structure in which the items contained are related to each other and that relationship allows for the data to be quickly and efficiently queried and retrieved for use. itself—it only removes the connection from the current project.
By using folder and database electronic storage container with a top-down structure in which the items contained are related to each other and that relationship allows for the data to be quickly and efficiently queried and retrieved for use. connections efficiently, ArcGIS Pro makes it easier to organize GIS Geographic Information Systems the software used to create, store, and manage spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. , analyze spatial problems, and display the data in cartographic layouts Geographic Information Sciences data, reducing the time spent searching for files and improving overall project workflow.
| Figure 4.6: ArcGIS Pro's Catalog View Basic Layout |
|---|
 |
