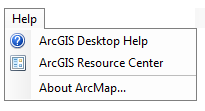
In order to become a GIS Geographic Information Systems the software used to create, store, and manage spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. , analyze spatial problems, and display the data in cartographic layouts Geographic Information Sciences pro, utilizing the built-in help is essential. When ArcGIS is installed on a computer, the local help is also installed. Found in the Help menu in the menu bar, the "ArcGIS Desktop Help" option will open the local help. By opening the books along the left side will get you the help topic you need. If you know the name of the tool or action you are looking for, you can search for it in the Search tab.
| Figure 4.16: ArcGIS Local Help Menu | |
|---|---|
 |
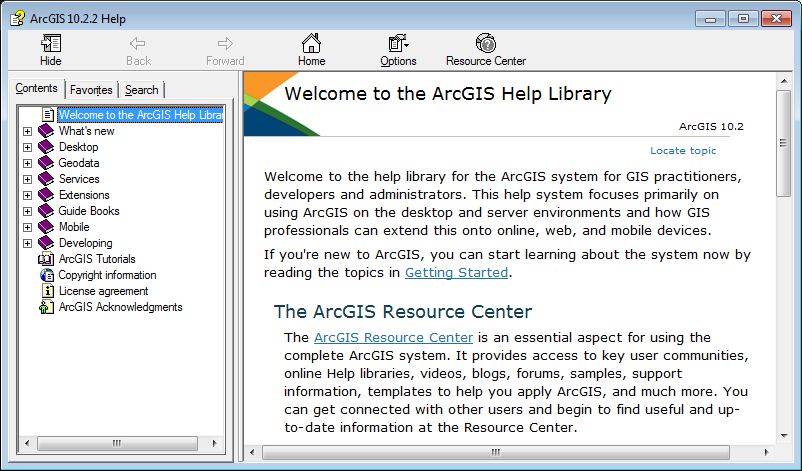 |
| The Help Menu option in the Help Drop Down Menu | The ArcGIS built in help menu (archaic looking, but still how it comes) |
Another version of the help menu is available online at https://desktop.arcgis.com/en/arcmap/latest/get-started/main/get-started-with-arcmap.htm This page is updated when ever it is needed, versus the built in help, which is only updated upon software updates. Notice the tabs across the top:
| Figure 4.17: ArcGIS Online Help Menu | |
|---|---|
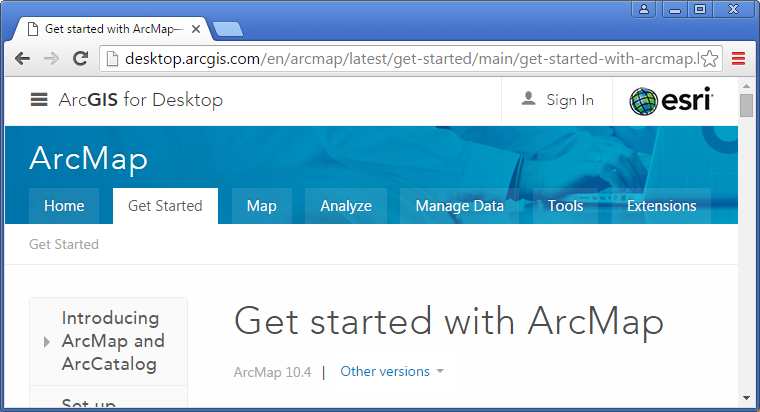 |
|
| The ArcGIS Online Help Menu | |
| Get Started | Articles which help with the layout and customization of ArcMap and ArcCatalog. |
|
ArcGIS Desktop Link: https://desktop.arcgis.com/en/arcmap/latest/get-started/main/get-started-with-arcmap.htm |
|
| Map | Articles which help with basic operational functions of ArcMap (Heading: Work with ArcMap) and information about creating layouts (cartographic products) in ArcMap (Headings: Page Layouts and below |
|
ArcGIS Desktop Link: https://desktop.arcgis.com/en/arcmap/latest/map/main/mapping-and-visualization-in-arcgis-for-desktop.htm |
|
| Analyze | Articles which help you understand the basics of finding and executing geoprocessing tools. A handy bunch of articles when you're first starting out with the GIS Geographic Information Systems the software used to create, store, and manage spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. , analyze spatial problems, and display the data in cartographic layouts Geographic Information Sciences . |
| ArcGIS Desktop Link: https://desktop.arcgis.com/en/arcmap/latest/analyze/main/what-is-geoprocessing.htm ArcGIS Pro Link: No equivalent |
|
| Manage Data | Articles which help you understand the different types of spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. used in the GIS Geographic Information Systems the software used to create, store, and manage spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. , analyze spatial problems, and display the data in cartographic layouts Geographic Information Sciences , which include but are not limited to vector (feature classes and shapefiles), raster, and data tables. |
|
ArcGIS Desktop Link: https://desktop.arcgis.com/en/arcmap/latest/manage-data/main/what-is-geodata.htm |
|
| Tools | Articles which help with the various geoprocessing tools used in ArcGIS software. These are the articles you will be referring to for a very long time. Even though this really good article about how to read the help menu pages for geoprocessing tools was written for the ArcGIS Pro help page, the information is the same for both the ArcGIS Desktop and ArcGIS Pro pages. |
|
ArcGIS Desktop Link: https://desktop.arcgis.com/en/arcmap/latest/tools/main/a-quick-tour-of-geoprocessing-tool-references.htm |
|
| Extensions |
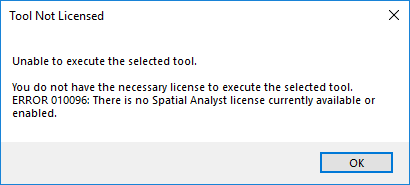
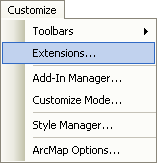
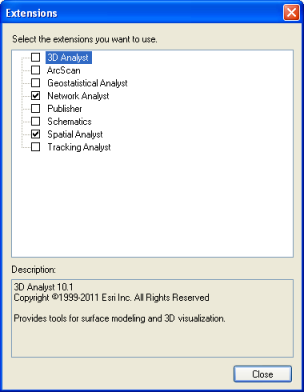
An explanation of the various extensions in ArcGIS. ArcGIS, a proprietary software, costs money, unlike a opens source software like QGIS. And it costs a fair amount of money. With the exception of K-12 school and humanitarian non-profits, companies need to pay for not only the base software, but also for any upgrades and additional advanced toolboxes. In order to save costs, companies can elect to purchase the number of base licenses they need to match the number of employees and then just a few copies of the more advanced tools (called extensions to share among everyone. This sharing process, in ArcGIS, is referred to as enabling extensions. When an extension is enabled on one machine by a single technician on a shared company network, that extension cannot be used by any other technician on the same network until it is disabled by the first technician. Think about it like a public library - Instead of purchasing tons of copies of one particular best-seller, they purchase a limited number of copies, then lend them out free of charge to their registered users. While the book is checked out, no one else can read it, as it is not physically available to any other reader while in possession of the first reader. ArcGIS extensions work the same way - limited count extensions are only available to a few technicians at a time to check out (enable) and cannot be used by another technician until it is checked back in (disabled). |
|
ArcGIS Desktop Link: https://desktop.arcgis.com/en/arcmap/latest/extensions/main/about-arcgis-for-desktop-extensions.htm HOWEVER ArcGIS Pro authorizes extensions with the .prvc license file instead of using the extensions functionality. This is why it's important to authorize your ArcGIS Pro student software as Single Use with the .prvc file and NOT just signing in (which includes basic operations, no extensions) |
When you visit the online help, you will notice it is set up a lot like this wiki (the other way around, really). That was an intentional effort to help make the transition from GIS Geographic Information Systems the software used to create, store, and manage spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. , analyze spatial problems, and display the data in cartographic layouts Geographic Information Sciences 101 to utilizing the GIS Geographic Information Systems the software used to create, store, and manage spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. , analyze spatial problems, and display the data in cartographic layouts Geographic Information Sciences help seamless.
When it comes to learning to use the software beyond this class, the ArcGIS help menu is the best resource out there (beyond taking more GIS Geographic Information Systems the software used to create, store, and manage spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. , analyze spatial problems, and display the data in cartographic layouts Geographic Information Sciences classes, but even then, you’ll use the help menu). I, and every GIS Geographic Information Systems the software used to create, store, and manage spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. , analyze spatial problems, and display the data in cartographic layouts Geographic Information Sciences technician/analyst I know, use the help on a very regular basis, if not daily. From looking up tools to remember which tool does what to finding the proper Python syntax when writing custom tools, ESRI has done a really good job with the help menu. Throughout the wiki, you will find links to ArcGIS help articles for various tools and processes. Clicking through the link and skimming the article is considered mandatory in this class, since the overall goal is to prepare you to be an independent GIS Geographic Information Systems the software used to create, store, and manage spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. , analyze spatial problems, and display the data in cartographic layouts Geographic Information Sciences user. Learning to read help articles is fundamental to the process of developing good software skills.