The spatial distribution of both raster and vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects can be categorized into two types: discrete data Discrete data, which is sometimes called thematic, categorical, or discontinuous data, most often represents objects in both the feature (vector) and raster data Raster data is a type of digital data that stores information about a location using a grid of pixels or cells. All spatial rasters are raster files, but not all raster files are spatial rasters. storage systems. A discrete object has known and definable boundaries: it is easy to define precisely where the object begins and where it ends. and continuous data A continuous surface represents phenomena in which each location on the surface is a measure of the concentration level or its relationship from a fixed point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. in space or from an emitting source. . While either type of spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. can contain discrete or continuous features, vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects is typically associated with discrete data Discrete data, which is sometimes called thematic, categorical, or discontinuous data, most often represents objects in both the feature (vector) and raster data Raster data is a type of digital data that stores information about a location using a grid of pixels or cells. All spatial rasters are raster files, but not all raster files are spatial rasters. storage systems. A discrete object has known and definable boundaries: it is easy to define precisely where the object begins and where it ends. , while raster data Raster data is a type of digital data that stores information about a location using a grid of pixels or cells. All spatial rasters are raster files, but not all raster files are spatial rasters. is often used for continuous data A continuous surface represents phenomena in which each location on the surface is a measure of the concentration level or its relationship from a fixed point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. in space or from an emitting source. .
3.4.1: Discrete Data
Discrete data represents features that exist as individual, separate entities with clear, definable boundaries—even when they are part of a larger dataset. For example, a vector layer showing the continental United States is considered discrete data Discrete data, which is sometimes called thematic, categorical, or discontinuous data, most often represents objects in both the feature (vector) and raster data Raster data is a type of digital data that stores information about a location using a grid of pixels or cells. All spatial rasters are raster files, but not all raster files are spatial rasters. storage systems. A discrete object has known and definable boundaries: it is easy to define precisely where the object begins and where it ends. . Each state has a well-defined boundary, and removing one state does not affect the existence of the others. Similarly, a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. , line, or polygon feature exists independently within a dataset, meaning discrete data Discrete data, which is sometimes called thematic, categorical, or discontinuous data, most often represents objects in both the feature (vector) and raster data Raster data is a type of digital data that stores information about a location using a grid of pixels or cells. All spatial rasters are raster files, but not all raster files are spatial rasters. storage systems. A discrete object has known and definable boundaries: it is easy to define precisely where the object begins and where it ends. can take any vector geometry form:
- Points: Represent locations such as fire hydrants, trees, or cities.
- Polylines: Represent linear features such as rivers, roads, or trails.
- Polygons: Represent area-based features such as lakes, buildings, or administrative boundaries.
Raster data can also be discrete, though it is less common. In these cases, raster pixels contain categorical values representing distinct features, such as land use classifications (e.g., "Forest," "Urban," "Water").
3.4.2: Continuous Data
Continuous data is the opposite of discrete data Discrete data, which is sometimes called thematic, categorical, or discontinuous data, most often represents objects in both the feature (vector) and raster data Raster data is a type of digital data that stores information about a location using a grid of pixels or cells. All spatial rasters are raster files, but not all raster files are spatial rasters. storage systems. A discrete object has known and definable boundaries: it is easy to define precisely where the object begins and where it ends. . It does not have clear, defined boundaries but instead forms a continuous surface across a landscape, where values transition gradually rather than existing as distinct units. Unlike discrete data Discrete data, which is sometimes called thematic, categorical, or discontinuous data, most often represents objects in both the feature (vector) and raster data Raster data is a type of digital data that stores information about a location using a grid of pixels or cells. All spatial rasters are raster files, but not all raster files are spatial rasters. storage systems. A discrete object has known and definable boundaries: it is easy to define precisely where the object begins and where it ends. , removing a portion of continuous data A continuous surface represents phenomena in which each location on the surface is a measure of the concentration level or its relationship from a fixed point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. in space or from an emitting source. does not eliminate the concept itself.
For example, consider temperature data. If you remove a specific temperature value, such as 75°F, from a dataset, the concept of 75°F still exists in reality. This is different from removing a state boundary—if you erased Colorado and redrew the map, future generations may not recognize "Colorado" as a distinct entity. However, the concept of temperature remains the same regardless of classification.
Examples of continuous data A continuous surface represents phenomena in which each location on the surface is a measure of the concentration level or its relationship from a fixed point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. in space or from an emitting source. include:
- Temperature – Temperature values change gradually across a landscape.
- Precipitation – Rainfall varies across a region without distinct separations.
- Elevation – Land elevation the vertical distance between local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features and a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface is a continuous surface with gradual transitions.
- Slope & Aspect – Slope represents how steep an area is, while aspect [geographic coordinate systems] The direction the developable surface a geometric shape which will not be distorted when flattened. Used as the base shape to transfer features during projections. Most often a cone, cylinder, or plane (azimuthal) faces in relation to the geographic coordinate system. Normal; transverse, oblique[topography] The cardinal direction a slope A numeric value - either in percent or degree - expressing the steepness or the rise/run of the landscape. faces (NSEW) shows which direction a slope A numeric value - either in percent or degree - expressing the steepness or the rise/run of the landscape. faces.
Most classified raster data Raster data is a type of digital data that stores information about a location using a grid of pixels or cells. All spatial rasters are raster files, but not all raster files are spatial rasters. falls into the continuous category. From these continuous layers, we can extract information to create discrete data Discrete data, which is sometimes called thematic, categorical, or discontinuous data, most often represents objects in both the feature (vector) and raster data Raster data is a type of digital data that stores information about a location using a grid of pixels or cells. All spatial rasters are raster files, but not all raster files are spatial rasters. storage systems. A discrete object has known and definable boundaries: it is easy to define precisely where the object begins and where it ends. . For example, a Digital Elevation Model ( DEM Digital Elevation Model ) represents continuous elevation the vertical distance between local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features and a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface , but we can classify parts of it into discrete categories—such as identifying slopes between 10° and 40° as ideal nesting areas for birds.
| Figure 3.14: An Example of Discrete and Continuous Data Displayed on a Single Map |
|---|
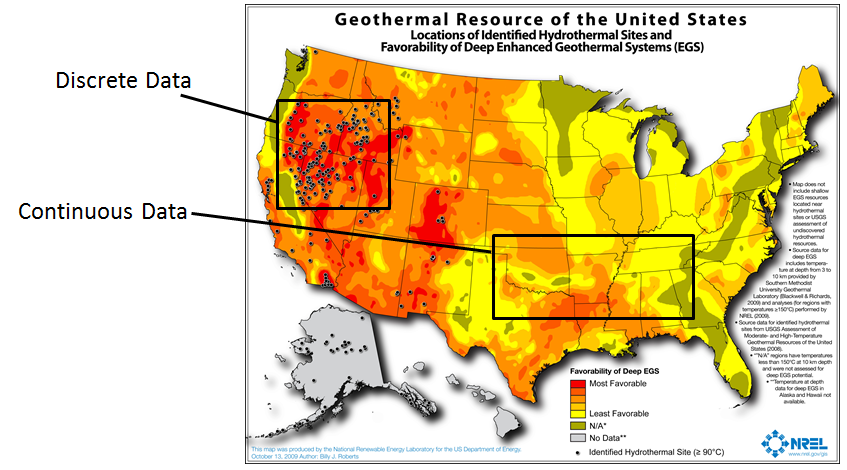 |
3.4.3: Understanding Continuous Data in GIS Geographic Information Systems the software used to create, store, and manage spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. , analyze spatial problems, and display the data in cartographic layouts Geographic Information Sciences
Students sometimes struggle with the fact that continuous data A continuous surface represents phenomena in which each location on the surface is a measure of the concentration level or its relationship from a fixed point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. in space or from an emitting source. often appears discrete in GIS Geographic Information Systems the software used to create, store, and manage spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. , analyze spatial problems, and display the data in cartographic layouts Geographic Information Sciences software. For example, the Geothermal Resources of the United States map (Figure 3.13) shows color-coded swirls of red, orange, yellow, and green that represent a continuous range of geothermal favorability. However, in reality, these colors do not stop abruptly—the data is continuous, but we must symbolize and generalize it to fit within the software’s display limitations.
Understanding the difference between continuous and discrete data Discrete data, which is sometimes called thematic, categorical, or discontinuous data, most often represents objects in both the feature (vector) and raster data Raster data is a type of digital data that stores information about a location using a grid of pixels or cells. All spatial rasters are raster files, but not all raster files are spatial rasters. storage systems. A discrete object has known and definable boundaries: it is easy to define precisely where the object begins and where it ends. is crucial in GIS Geographic Information Systems the software used to create, store, and manage spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. , analyze spatial problems, and display the data in cartographic layouts Geographic Information Sciences because many geoprocessing tools and cartographic processes are designed for one type of data over the other. The software processes them using different mathematical models, meaning certain operations only work with raster or vector formats.
| Figure 3.15: Examples of Discrete Data |
|---|
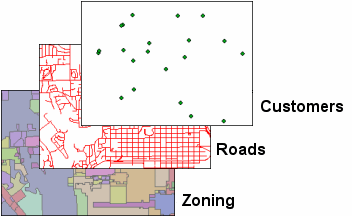 |
| Three examples of discrete data Discrete data, which is sometimes called thematic, categorical, or discontinuous data, most often represents objects in both the feature (vector) and raster data Raster data is a type of digital data that stores information about a location using a grid of pixels or cells. All spatial rasters are raster files, but not all raster files are spatial rasters. storage systems. A discrete object has known and definable boundaries: it is easy to define precisely where the object begins and where it ends. - point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. , polyline A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of two or more vertices connected by straight lines. Often used to represent objects such as roads, river, and boundaries. , and polygon. |
3.4.4: Special Cases – Continuous Vector Data & Discrete Raster Data
While most vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects is discrete and most raster data Raster data is a type of digital data that stores information about a location using a grid of pixels or cells. All spatial rasters are raster files, but not all raster files are spatial rasters. is continuous, there are exceptions:
- Continuous Vector Data
- Some vector datasets represent
continuous data
A continuous surface represents phenomena in which each location on the surface is a measure of the concentration level or its relationship from a fixed
point
A GIS
vector data
in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects
geometry type which is made up of just one
vertex
pl. vertices
One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature.
, marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system.
in space or from an emitting source.
, such as:
- Contour lines – These lines connect points of equal elevation the vertical distance between local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features and a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface .
- Triangulated Irregular Networks (TINs) – These show elevation the vertical distance between local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features and a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface as a continuous surface but use vector triangles instead of raster grids.
- Some vector datasets represent
continuous data
A continuous surface represents phenomena in which each location on the surface is a measure of the concentration level or its relationship from a fixed
point
A GIS
vector data
in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects
geometry type which is made up of just one
vertex
pl. vertices
One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature.
, marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system.
in space or from an emitting source.
, such as:
- Discrete Raster Data
- Certain raster datasets classify the landscape into distinct categories, making them discrete. Examples include:
- Land use maps – Representing categories like "Urban," "Forest," "Agriculture."
- Zoning maps – Dividing land into distinct regulatory classifications.
- Certain raster datasets classify the landscape into distinct categories, making them discrete. Examples include:
Triangulated Irregular Networks (TINs) and Contour Lines
A Triangulated Irregular Network (TIN) is a vector-based representation of continuous elevation the vertical distance between local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features and a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface . TINs are created from elevation the vertical distance between local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features and a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface points or DEM Digital Elevation Model data, forming a series of connected triangles that approximate the surface of the terrain. While TINs are useful for terrain modeling, they are not commonly used in beginner GIS Geographic Information Systems the software used to create, store, and manage spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. , analyze spatial problems, and display the data in cartographic layouts Geographic Information Sciences courses.
| Figure 3.16: A TIN with Contour Lines Drawn Over |
|---|
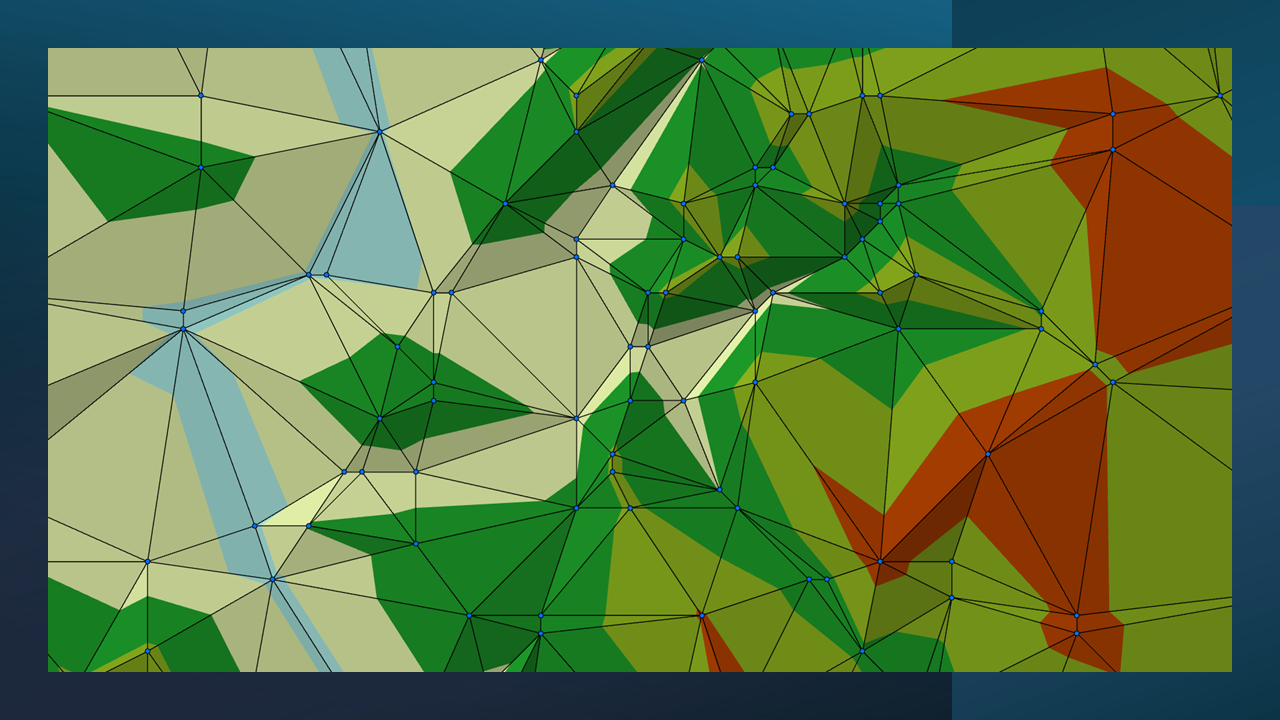 |
Contour Lines
Contour lines, on the other hand, are more familiar. These are vector-based representations of elevation the vertical distance between local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features and a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface that connect points of equal height. GIS Geographic Information Systems the software used to create, store, and manage spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. , analyze spatial problems, and display the data in cartographic layouts Geographic Information Sciences software generates contour lines from TINs, DEMs, or elevation the vertical distance between local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features and a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. datasets, using a process where the user specifies an interval (e.g., every 10, 50, or 100 meters). The result is a polyline A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of two or more vertices connected by straight lines. Often used to represent objects such as roads, river, and boundaries. layer that helps visualize elevation the vertical distance between local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features and a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface changes in a familiar format.
| Figure 3.17: A Very Close Up of Contour Lines Over an Elevation Point Layer |
|---|
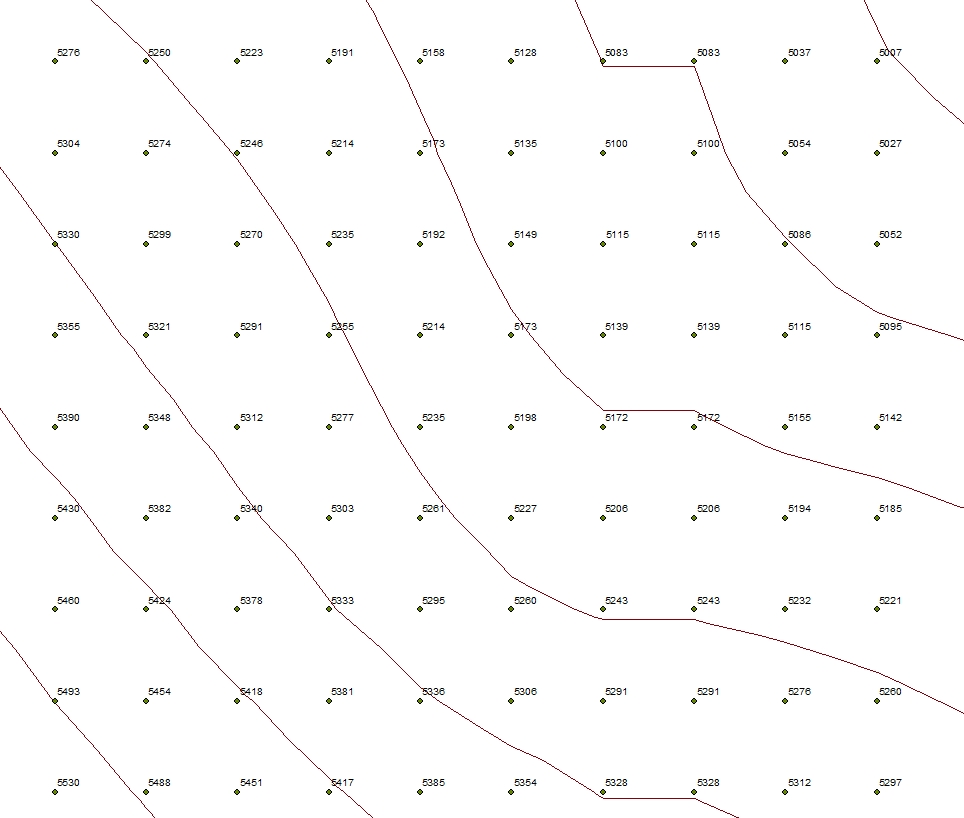 |
| Contour lines, whether created from a TIN, a DEM Digital Elevation Model , or a point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. layer, are all formed in the same way: point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. or pixels of equal elevation the vertical distance between local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features and a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface are determined by the software and then connected with lines. Each contour line represents one elevation the vertical distance between local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features and a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface , with the next having a |
