In Section Three, we looked at the idea that the Earth is not best represented by a sphere (or even a spheroid a sphere-like 3D object where the radius in one direction is longer than the radius in a direction at a right angle to the first ), but a geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." , which is a model of the variation in gravitational pull over the surface of the Earth. This variation allows for a modeling of true mean sea level at any single location on the Earth's surface, since an assumption could be made between the strength of the pull of gravity and where water would pool (higher gravitational pull, more water pooling).
We also noted the best way to simplify the shape is to match it to a 3D reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid , one which either was best-fit for the whole world (global reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid ) or one which was best-fit for a local area (local reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid - which could be regional, continental, state-wide, county wide, or city wide). We also learned that the reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid was great for laying out the 2D portion of the map and we mentioned that the geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." is the base for the Z value or elevation the vertical distance between local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features and a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface portion for making maps. In order to make useful maps, we need combine the 2D, XY half of the map and the 3D, Z half of the map. This is accomplished with the creation of a geodetic datum the result of attaching a "free-floating" reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid to a specifically measured geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." via control points and benchmarks. , or really just "datum" for short.
2.5.1: Geodetic Datums
So far, we understand 2D maps, consisting of the shapes of continents, states, counties, or city limits (among a whole boatload of other features), drawn on the reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid , while the elevation the vertical distance between local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features and a single point on the Earth's surface values are stored with the geodetic datums, or - what most people say - just "datums".
Reference ellipsoids come in two varieties - global, containing a map of all of the continents and oceans, and local, which consist of any are smaller than the whole globe. Geoids are almost always, and in our studies here will always, consists of the entire globe. When we create datums, the reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid is the half of the equation that decides the extent of the datum. If the reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid only covers North America, it most likely fits inside the geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." pretty darn good in North America but doesn't touch anywhere else in the world (or if it does, by chance, it is ignored). When the datum is created, the extent - the boundaries of the datum - is limited to North America, regardless of the fact that the geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." maps the elevation the vertical distance between local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features and a single point on the Earth's surface of the entire planet. If the extent of the reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid is the entire globe, it will fit mostly okay everywhere on Earth (the extent of the geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." ) - some place will be very close, some will be quite a bit off, and some will be average. But that is nature of global datums - kinda good everywhere, but not really great anywhere.
As we will see in the next section, the reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid is not blank to start, but actually covered with an evenly spaced Cartesian Coordinate System specifically called a geographic grid the result of using an established angular unit of measure to label the intersections of north-south and east-west lines on the surface of the Earth starting the labels at a principal meridian the north-south line from which the labeling begins. East-west lines have a very obvious start point: the equator. North-south lines must start somewhere, so when it is established for a particular geographic grid, it can be considered the principal meridian. . This grid is used to start the process of labeling exact locations on the Earth's surface, but in this section, we will just remember the reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid is not blank like a piece of printer paper, but covered in a grid like engineer's paper.
We haven't really talked much about the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." - the surface upon which we walk around and observe the Earth's landforms the descriptive words for individual features on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." , such as "hills", "valley", and "ridgelines" , but we need to remember that all of these mathematical models are created and used with the goal of labeling and navigating to locations on the Earth's surface. Since that is our goal, we need something to connect the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." to the geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." to the reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid , and that real-world object is a benchmark. Benchmarks are, as we said, real world objects that are placed and maintained at specific and known locations of the Earth's surface. Some benchmarks Benchmarks are real-world locations which have been carefully surveyed with locations to match a specific geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." . are labeled monuments, some are chunks of rebar sunk into concrete, and some are just chunks of concrete, but all of them are scattered about world-wide and are used to connect the three surfaces together.
As, I'm sure you've noticed, there are not benchmarks Benchmarks are real-world locations which have been carefully surveyed with locations to match a specific geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." . covering the entire surface of the Earth, and most likely, you've never actually noticed a benchmark in real life ever. Since they are not covering the Earth at every location, we use the ones which do exist, then mathematically infer the rest.
Every benchmark is at a known location upon an existing Cartesian Coordinate System, we can use them as a connection point between the geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." (a model of the difference between GMSL and LMSL via a model of gravitational acceleration) and the reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid (a gridded 3D shape with the oceans and land areas drawn upon it). If, for example, a benchmark existing on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." in the real world has an "address" (the exact known location) of -114.03, 34.42 which has been carefully surveyed and recorded, the geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." is created with GPS Global Positioning System: A satellite-based navigation system owned and operated by the United States Department of Defense that provides location and time information anywhere on Earth. (an electronic means of finding Earth "addresses"), and the reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid has a point marked on it's grid found by counting 34.42 intersections east of the 0,0 origin and 114.03 intersections south, we can simply connect the same location between the three different surfaces, creating beginning of a geodetic datum the result of attaching a "free-floating" reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid to a specifically measured geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." via control points and benchmarks. , or just datum. If we connect several benchmarks Benchmarks are real-world locations which have been carefully surveyed with locations to match a specific geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." . between the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." with the matching, known coordinates located on a specific geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." and some specific reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid , we have a pretty good start to the datum. If we know the "address" of each connected benchmark/ geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." coordinates/ reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid 's Cartesian Coordinate System coordinates, using simple counting we can label all the remaining intersections on the datum and call those mathematically derived connections control points. And you thought you'd never use Cartesian Coordinate Systems again.....
-
- NOTE: Benchmarks are used for the basis of all datums. Once a benchmark is used to make the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." - geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." - reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid connection, it is "converted" into a control point aka: tie point mathematically derived points that connect a two spatial objects together, such as a geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." and a reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid . The difference between the two is a benchmark an actual object which resides in the real world and is used over and over to create lots of datums and a control point aka: tie point mathematically derived points that connect a two spatial objects together, such as a geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." and a reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid is a mathematically determined connection between a geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." and a reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid which "resides" in the datum. So, within a datum, all benchmarks Benchmarks are real-world locations which have been carefully surveyed with locations to match a specific geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." . become control points, but not all control points started out as benchmarks Benchmarks are real-world locations which have been carefully surveyed with locations to match a specific geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." . .
| The Main Point... |
|---|
| Datums are: reference ellipsoids that have been linked to a specific geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." via control points, which connect real-world points called benchmarks Benchmarks are real-world locations which have been carefully surveyed with locations to match a specific geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." . with mathematically derived points on the reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid . |
List of Supported Datums
View as a Separate Page| Datum Name | WKID | Spheroid Name |
|---|---|---|
| 1_Ceres_2015 | 106972 | 1_Ceres_2015 |
| 4_Vesta_2015 | 106973 | 4_Vesta_2015 |
| D_Abidjan_1987 | 6143 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| AbInvA96_2020_Intermediate_Reference_Frame | 1273 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Accra | 6168 | War_Office |
| D_Aden_1925 | 1135 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Adindan | 6201 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Adrastea_2000 | 106909 | Adrastea_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Afgooye | 6205 | Krasovsky_1940 |
| D_Agadez | 6206 | Clarke_1880_IGN |
| D_Ain_el_Abd_1970 | 6204 | International_1924 |
| D_Airy_1830 | 6001 | Airy_1830 |
| D_Airy_Modified | 6002 | Airy_Modified |
| D_Alaskan_Islands | 106260 | Clarke_1866 |
| D_Albanian_1987 | 6191 | Krasovsky_1940 |
| D_Amalthea_2000 | 106910 | Amalthea_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_American_Samoa_1962 | 6169 | Clarke_1866 |
| D_Amersfoort | 6289 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_Ammassalik_1958 | 6196 | International_1924 |
| D_Ananke_2000 | 106911 | Ananke_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Anguilla_1957 | 6600 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Anna_1_1965 | 6708 | Australian |
| D_Antigua_1943 | 6601 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Aratu | 6208 | International_1924 |
| D_Arc_1950 | 6209 | Clarke_1880_Arc |
| D_Arc_1960 | 6210 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Ariel_2000 | 106945 | Ariel_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Ascension_Island_1958 | 6712 | International_1924 |
| D_Astro_1952 | 6711 | International_1924 |
| D_ATF | 6901 | Plessis_1817 |
| D_Atlas_2000 | 106926 | Atlas_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_ATS_1977 | 6122 | ATS_1977 |
| D_Australian | 6003 | Australian |
| D_Australian_1966 | 6202 | Australian |
| D_Australian_1984 | 6203 | Australian |
| D_Australian_Antarctic_1998 | 6176 | GRS_1980 |
| Australian_Terrestrial_Reference_Frame_2014 | 1291 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Ayabelle | 6713 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Azores_Central_Islands_1948 | 6183 | International_1924 |
| D_Azores_Central_Islands_1995 | 6665 | International_1924 |
| D_Azores_Occidental_Islands_1939 | 6182 | International_1924 |
| D_Azores_Oriental_Islands_1940 | 6184 | International_1924 |
| D_Azores_Oriental_Islands_1995 | 6664 | International_1924 |
| D_Bab_South | 106269 | Clarke_1866 |
| D_Barbados_1938 | 6212 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Batavia | 6211 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_Beacon_E_1945 | 6709 | International_1924 |
| D_Beduaram | 6213 | Clarke_1880_IGN |
| D_Beijing_1954 | 6214 | Krasovsky_1940 |
| D_Bekaa_Valley_1920 | 1137 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Belge_1950 | 6215 | International_1924 |
| D_Belge_1972 | 6313 | International_1924 |
| D_Belinda_2000 | 106946 | Belinda_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Bellevue_IGN | 6714 | International_1924 |
| D_Bermuda_1957 | 6216 | Clarke_1866 |
| D_Bermuda_2000 | 6762 | WGS_1984 |
| D_Bern_1898 | 6217 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_Bern_1938 | 6306 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_Bessel_1841 | 6004 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_Bessel_Modified | 6005 | Bessel_Modified |
| D_Bessel_Namibia | 6006 | Bessel_Namibia |
| D_Bhutan_National_Geodetic_Datum | 1058 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Bianca_2000 | 106947 | Bianca_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Bioko | 1136 | International_1924 |
| D_Bissau | 6165 | International_1924 |
| D_Bogota | 6218 | International_1924 |
| D_Bukit_Rimpah | 6219 | Bessel_1841 |
| Bulgaria_Geodetic_System_2005 | 1167 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Cadastre_1997 | 1037 | International_1924 |
| California_SRS_Epoch_2017.50_(NAD83) | 106012 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Callisto_2000 | 106912 | Callisto_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Calypso_2000 | 106927 | Calypso_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Camacupa | 6220 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| Camacupa_2015 | 1217 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Camp_Area | 6715 | International_1924 |
| D_Campo_Inchauspe | 6221 | International_1924 |
| D_Canton_1966 | 6716 | International_1924 |
| D_Cape | 6222 | Clarke_1880_Arc |
| D_Cape_Canaveral | 6717 | Clarke_1866 |
| D_Carme_2000 | 106913 | Carme_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Carthage | 6223 | Clarke_1880_IGN |
| D_Cayman_Islands_Geodetic_Datum_2011 | 1100 | GRS_1980 |
| D_CH1903 | 6149 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_CH1903+ | 6150 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_Charon_2000 | 106970 | Charon_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Chatham_Island_1971 | 6672 | International_1924 |
| D_Chatham_Islands_1979 | 6673 | International_1924 |
| D_China_2000 | 1043 | CGCS2000 |
| D_Chos_Malal_1914 | 6160 | International_1924 |
| D_Chua | 6224 | International_1924 |
| D_Clarke_1858 | 6007 | Clarke_1858 |
| D_Clarke_1866 | 6008 | Clarke_1866 |
| D_Clarke_1866_Michigan | 6009 | Clarke_1866_Michigan |
| D_Clarke_1880 | 6034 | Clarke_1880 |
| D_Clarke_1880_Arc | 6013 | Clarke_1880_Arc |
| D_Clarke_1880_Benoit | 6010 | Clarke_1880_Benoit |
| D_Clarke_1880_IGN | 6011 | Clarke_1880_IGN |
| D_Clarke_1880_RGS | 6012 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Clarke_1880_SGA | 6014 | Clarke_1880_SGA |
| D_Combani_1950 | 6632 | International_1924 |
| D_Conakry_1905 | 6315 | Clarke_1880_IGN |
| D_Cordelia_2000 | 106948 | Cordelia_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Corrego_Alegre | 6225 | International_1924 |
| D_Corrego_Alegre_1961 | 1074 | International_1924 |
| D_Costa_Rica_2005 | 1065 | WGS_1984 |
| D_Cote_d_Ivoire | 6226 | Clarke_1880_IGN |
| D_Cressida_2000 | 106949 | Cressida_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Croatian_Terrestrial_Reference_System | 6761 | GRS_1980 |
| CR-SIRGAS | 1225 | GRS_1980 |
| D_CSG_1967 | 6623 | International_1924 |
| D_Cyprus_Geodetic_Reference_System_1993 | 1112 | WGS_1984 |
| D_D48 | 106278 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_Dabola_1981 | 6155 | Clarke_1880_IGN |
| D_Datum_73 | 6274 | International_1924 |
| D_Datum_Geodesi_Nasional_1995 | 6755 | WGS_1984 |
| D_Datum_Lisboa_Bessel | 106262 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_Datum_Lisboa_Hayford | 106263 | International_1924 |
| D_Dealul_Piscului_1933 | 6316 | International_1924 |
| D_Dealul_Piscului_1970 | 6317 | Krasovsky_1940 |
| D_Deception_Island | 6736 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Deimos_2000 | 106906 | Deimos_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Deir_ez_Zor | 6227 | Clarke_1880_IGN |
| D_Desdemona_2000 | 106950 | Desdemona_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Despina_2000 | 106961 | Despina_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Deutsche_Bahn_Reference_System | 1081 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_Deutsches_Hauptdreiecksnetz | 6314 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_Dione_2000 | 106928 | Dione_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Dominica_1945 | 6602 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_DOS_1968 | 106218 | International_1924 |
| D_DOS_71_4 | 6710 | International_1924 |
| D_Douala | 6228 | Clarke_1880_IGN |
| D_Douala_1948 | 6192 | International_1924 |
| D_Easter_Island_1967 | 6719 | International_1924 |
| ECML14_NB_Intermediate_Reference_Frame | 1310 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Egypt_1907 | 6229 | Helmert_1906 |
| D_Egypt_1930 | 6199 | International_1924 |
| D_Egypt_Gulf_of_Suez_S-650_TL | 6706 | Helmert_1906 |
| D_Elara_2000 | 106914 | Elara_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Enceladus_2000 | 106929 | Enceladus_2000_IAU_IAG |
| EOS21_Intermediate_Reference_Frame | 1308 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Epimetheus_2000 | 106930 | Epimetheus_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Estonia_1937 | 106101 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_Estonia_1992 | 6133 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Estonia_1997 | 6180 | GRS_1980 |
| D_ETRF_1989 | 1178 | WGS_1984 |
| ETRF2000_Poland | 1305 | GRS_1980 |
| D_ETRS_1989 | 6258 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Europa_2000 | 106915 | Europa_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_European_1950 | 6230 | International_1924 |
| D_European_1950_ED77 | 6154 | International_1924 |
| D_European_1979 | 6668 | International_1924 |
| D_European_1987 | 6231 | International_1924 |
| D_European_Libyan_1979 | 6159 | International_1924 |
| European_Terrestrial_Reference_Frame_1990 | 1179 | GRS_1980 |
| European_Terrestrial_Reference_Frame_1991 | 1180 | GRS_1980 |
| European_Terrestrial_Reference_Frame_1992 | 1181 | GRS_1980 |
| European_Terrestrial_Reference_Frame_1993 | 1182 | GRS_1980 |
| European_Terrestrial_Reference_Frame_1994 | 1183 | GRS_1980 |
| European_Terrestrial_Reference_Frame_1996 | 1184 | GRS_1980 |
| European_Terrestrial_Reference_Frame_1997 | 1185 | GRS_1980 |
| European_Terrestrial_Reference_Frame_2000 | 1186 | GRS_1980 |
| European_Terrestrial_Reference_Frame_2005 | 1204 | GRS_1980 |
| European_Terrestrial_Reference_Frame_2014 | 1206 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Everest_1830 | 6042 | Everest_1830 |
| D_Everest_Adj_1937 | 6015 | Everest_Adjustment_1937 |
| D_Everest_Bangladesh | 106202 | Everest_Adjustment_1937 |
| D_Everest_Def_1962 | 6044 | Everest_Definition_1962 |
| D_Everest_Def_1967 | 6016 | Everest_Definition_1967 |
| D_Everest_Def_1975 | 6045 | Everest_Definition_1975 |
| D_Everest_India_Nepal | 106203 | Everest_Definition_1962 |
| D_Everest_Modified | 6018 | Everest_1830_Modified |
| D_Everest_Modified_1969 | 106006 | Everest_Modified_1969 |
| EWR2_Intermediate_Reference_Frame | 1311 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Fahud | 6232 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Faroe_Datum_1954 | 6741 | International_1924 |
| D_Fatu_Iva_1972 | 6688 | International_1924 |
| D_FD_1958 | 6132 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Fehmarnbelt_Datum_2010 | 1078 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Fiji_1956 | 6721 | International_1924 |
| D_Fiji_1986 | 6720 | WGS_1972 |
| D_Fischer_1960 | 106002 | Fischer_1960 |
| D_Fischer_1968 | 106003 | Fischer_1968 |
| D_Fischer_Modified | 106004 | Fischer_Modified |
| D_fk89 | 6753 | International_1924 |
| D_Fort_Desaix | 6625 | International_1924 |
| D_Fort_Marigot | 6621 | International_1924 |
| D_Fort_Thomas_1955 | 106240 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Galatea_2000 | 106962 | Galatea_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Gambia | 1139 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Gan_1970 | 6684 | International_1924 |
| D_Ganymede_2000 | 106916 | Ganymede_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Garoua | 6197 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| GBK19_Intermediate_Reference_Frame | 1289 | GRS_1980 |
| D_GDA_1994 | 6283 | GRS_1980 |
| GDA2020 | 1168 | GRS_1980 |
| D_GDBD2009 | 1056 | GRS_1980 |
| D_GDM_2000 | 6742 | GRS_1980 |
| D_GEM_10C | 6031 | GEM_10C |
| Geocentric_Datum_of_Mauritius_2008 | 106028 | GRS_1980 |
| Geodezicheskaya_Sistema_Koordinat_2011 | 1159 | GSK-2011 |
| Georgia_Geodetic_Datum | 106010 | GRS_1980 |
| D_GGRS_1987 | 6121 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Graciosa_Base_SW_1948 | 106241 | International_1924 |
| D_Grand_Cayman_1959 | 6723 | Clarke_1866 |
| D_Grand_Comoros | 6646 | International_1924 |
| D_Greek | 6120 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_Greenland_1996 | 6747 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Grenada_1953 | 6603 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_GRS_1967 | 6036 | GRS_1967 |
| D_GRS_1980 | 6019 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Guam_1963 | 6675 | Clarke_1866 |
| D_Gulshan_303 | 6682 | Everest_Adjustment_1937 |
| D_Gunung_Segara | 6613 | Bessel_1841 |
| Gusterberg_(Ferro) | 1188 | Zach_1812 |
| D_GUX_1 | 106221 | International_1924 |
| D_Guyane_Francaise | 6235 | International_1924 |
| D_Hanoi_1972 | 6147 | Krasovsky_1940 |
| D_Hartebeesthoek_1994 | 6148 | WGS_1984 |
| D_Helene_2000 | 106931 | Helene_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Helle_1954 | 6660 | International_1924 |
| D_Helmert_1906 | 6020 | Helmert_1906 |
| D_Herat_North | 6255 | International_1924 |
| D_Hermannskogel | 106102 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_Himalia_2000 | 106917 | Himalia_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Hito_XVIII_1963 | 6254 | International_1924 |
| D_Hjorsey_1955 | 6658 | International_1924 |
| D_Hong_Kong_1963 | 6738 | Clarke_1858 |
| D_Hong_Kong_1963_67 | 6739 | International_1924 |
| D_Hong_Kong_1980 | 6611 | International_1924 |
| Hong_Kong_Geodetic | 1209 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Hough_1960 | 106005 | Hough_1960 |
| HS2_Intermediate_Reference_Frame | 1264 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Hughes_1980 | 6054 | Hughes_1980 |
| D_Hungarian_1972 | 6237 | GRS_1967 |
| D_Hungarian_Datum_1909 | 1024 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_Hu_Tzu_Shan | 6236 | International_1924 |
| D_Hyperion_2000 | 106932 | Hyperion_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Iapetus_2000 | 106933 | Iapetus_2000_IAU_IAG |
| IG05(2012)_Intermediate_Datum | 1144 | GRS_1980 |
| IG05_Intermediate_Datum | 1142 | GRS_1980 |
| IGb00 | 1246 | GRS_1980 |
| IGb08 | 1248 | GRS_1980 |
| IGb14 | 1272 | GRS_1980 |
| D_IGC_1962_Arc_of_the_6th_Parallel_South | 6697 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_IGM_1995 | 6670 | WGS_1984 |
| D_IGN53_Mare | 6641 | International_1924 |
| D_IGN56_Lifou | 6633 | International_1924 |
| D_IGN63_Hiva_Oa | 6689 | International_1924 |
| D_IGN72_Grande_Terre | 6634 | International_1924 |
| D_IGN72_Nuku_Hiva | 6630 | International_1924 |
| D_IGN_Astro_1960 | 6700 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| IGS00 | 1245 | GRS_1980 |
| IGS05 | 1247 | GRS_1980 |
| IGS08 | 1141 | GRS_1980 |
| IGS14 | 1191 | GRS_1980 |
| IGS97 | 1244 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Indian_1954 | 6239 | Everest_Adjustment_1937 |
| D_Indian_1960 | 6131 | Everest_Adjustment_1937 |
| D_Indian_1975 | 6240 | Everest_Adjustment_1937 |
| D_Indonesian | 6021 | Indonesian |
| D_Indonesian_1974 | 6238 | Indonesian |
| D_Institut_Geographique_du_Congo_Belge_1955 | 6701 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_International_1924 | 6022 | International_1924 |
| D_International_1967 | 6023 | International_1967 |
| International_Terrestrial_Reference_Frame_2014 | 1165 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Io_2000 | 106918 | Io_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Iraqi_Geospatial_Reference_System | 1029 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Iraq_Kuwait_Boundary_1992 | 6667 | WGS_1984 |
| D_IRENET95 | 6173 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Islands_Network_1993 | 6659 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Islands_Network_2004 | 1060 | GRS_1980 |
| Islands_Net_2016 | 1187 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Israel | 6141 | GRS_1980 |
| Israel_Geodetic_Datum_2005 | 1114 | GRS_1980 |
| Israeli_Geodetic_Datum_2005(2012) | 1115 | GRS_1980 |
| D_ISTS_061_1968 | 6722 | International_1924 |
| D_ISTS_073_1969 | 6724 | International_1924 |
| D_ITRF_1988 | 6647 | GRS_1980 |
| D_ITRF_1989 | 6648 | GRS_1980 |
| D_ITRF_1990 | 6649 | GRS_1980 |
| D_ITRF_1991 | 6650 | GRS_1980 |
| D_ITRF_1992 | 6651 | GRS_1980 |
| D_ITRF_1993 | 6652 | GRS_1980 |
| D_ITRF_1994 | 6653 | GRS_1980 |
| D_ITRF_1996 | 6654 | GRS_1980 |
| D_ITRF_1997 | 6655 | GRS_1980 |
| D_ITRF_2000 | 6656 | GRS_1980 |
| D_ITRF_2005 | 6896 | GRS_1980 |
| D_ITRF_2008 | 1061 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Jamaica_1875 | 6241 | Clarke_1880 |
| D_Jamaica_1969 | 6242 | Clarke_1866 |
| D_Jamaica_2001 | 6758 | WGS_1984 |
| D_Janus_2000 | 106934 | Janus_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_JGD_2000 | 6612 | GRS_1980 |
| D_JGD_2011 | 1128 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Johnston_Island_1961 | 6725 | International_1924 |
| D_Jordan | 106277 | International_1924 |
| D_Jouik_1961 | 6679 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Juliet_2000 | 106951 | Juliet_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Jupiter_2000 | 106908 | Jupiter_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Kalianpur_1880 | 6243 | Everest_1830 |
| D_Kalianpur_1937 | 6144 | Everest_Adjustment_1937 |
| D_Kalianpur_1962 | 6145 | Everest_Definition_1962 |
| D_Kalianpur_1975 | 6146 | Everest_Definition_1975 |
| D_Kandawala | 6244 | Everest_Adjustment_1937 |
| D_Karbala_1979_Polservice | 6743 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Kasai_1953 | 6696 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Katanga_1955 | 6695 | Clarke_1866 |
| D_Kerguelen_Island_1949 | 6698 | International_1924 |
| D_Kertau | 6245 | Everest_1830_Modified |
| D_Kertau_RSO | 6751 | Everest_Modified_1969 |
| Kingdom_of_Saudi_Arabia_Geodetic_Reference_ Frame_2017 | 1268 | GRS_1980 |
| D_KKJ | 6123 | International_1924 |
| D_Korea_2000 | 6737 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Korean_Datum_1985 | 6162 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_Korean_Datum_1995 | 6166 | WGS_1984 |
| Kosovo_Reference_System_2001 | 1251 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Kousseri | 6198 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Krasovsky_1940 | 6024 | Krasovsky_1940 |
| D_Kusaie_1951 | 6735 | International_1924 |
| D_Kuwait_Oil_Company | 6246 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Kuwait_Utility | 6319 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Kyrgyz_Republic_2006 | 106009 | GRS_1980 |
| D_La_Canoa | 6247 | International_1924 |
| D_Lake | 6249 | International_1924 |
| D_Lao_1993 | 6677 | Krasovsky_1940 |
| D_Lao_National_Datum_1997 | 6678 | Krasovsky_1940 |
| D_Larissa_2000 | 106963 | Larissa_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Latvia_1992 | 6661 | GRS_1980 |
| D_LC5_1961 | 106243 | Clarke_1866 |
| D_Leda_2000 | 106919 | Leda_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Leigon | 6250 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Le_Pouce_1934 | 6699 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Liberia_1964 | 6251 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Libyan_Geodetic_Datum_2006 | 6754 | International_1924 |
| D_Lisbon | 6207 | International_1924 |
| D_Lisbon_1890 | 6666 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_Lithuania_1994 | 6126 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Little_Cayman_1961 | 6726 | Clarke_1866 |
| D_Locodjo_1965 | 6142 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Loma_Quintana | 6288 | International_1924 |
| D_Lome | 6252 | Clarke_1880_IGN |
| D_Luxembourg_1930 | 6181 | International_1924 |
| D_Luzon_1911 | 6253 | Clarke_1866 |
| Lyon_Turin_Ferroviaire_2004 | 1295 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Lysithea_2000 | 106920 | Lysithea_2000_IAU_IAG |
| Macao_1920 | 1207 | International_1924 |
| D_MACAO_2008 | 1208 | International_1924 |
| D_Madeira_1936 | 6185 | International_1924 |
| D_Madrid_1870 | 6903 | Struve_1860 |
| D_Madzansua | 6128 | Clarke_1866 |
| D_MAGNA | 6686 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Mahe_1971 | 6256 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Majuro | 106270 | Clarke_1866 |
| D_Makassar | 6257 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_Malongo_1987 | 6259 | International_1924 |
| D_Manoca | 6260 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Manoca_1962 | 6193 | Clarke_1880_IGN |
| D_Marco_Geodesico_Nacional | 1063 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Mars_1979 | 106904 | Mars_1979_IAU_IAG |
| D_Mars_2000 | 106905 | Mars_2000_IAU_IAG |
| Mars_2000_(Sphere) | 106971 | Mars_2000_(Sphere) |
| D_Massawa | 6262 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_Maupiti_1983 | 6692 | International_1924 |
| D_Mauritania_1999 | 6702 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Merchich | 6261 | Clarke_1880_IGN |
| D_Mercury_2000 | 106900 | Mercury_2000_IAU_IAG |
| Mercury_2015 | 106974 | Mercury_2015 |
| D_Metis_2000 | 106921 | Metis_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Mexican_Datum_of_1993 | 1042 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Mexico_ITRF2008 | 1120 | GRS_1980 |
| D_MGI | 6312 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_MGI_1901 | 1031 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_Mhast_1951 | 6703 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Mhast_Offshore | 6705 | International_1924 |
| D_Mhast_Onshore | 6704 | International_1924 |
| D_Midway_1961 | 6727 | International_1924 |
| D_Mimas_2000 | 106935 | Mimas_2000_IAU_IAG |
| Ministerio_de_Marina_Norte | 1258 | International_1924 |
| Ministerio_de_Marina_Sur | 1259 | International_1924 |
| D_Minna | 6263 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Miranda_2000 | 106952 | Miranda_2000_IAU_IAG |
| MML07_Intermediate_Reference_Frame | 1271 | GRS_1980 |
| D_MOLDREF99 | 1032 | GRS_1980 |
| MOMRA_Terrestrial_Reference_Frame_2000 | 1218 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Monte_Mario | 6265 | International_1924 |
| D_Montserrat_1958 | 6604 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Moon_2000 | 106903 | Moon_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Moorea_1987 | 6691 | International_1924 |
| D_MOP78 | 6639 | International_1924 |
| D_Mount_Dillon | 6157 | Clarke_1858 |
| D_Moznet | 6130 | WGS_1984 |
| D_Mporaloko | 6266 | Clarke_1880_IGN |
| D_NAD_1927_CGQ77 | 6609 | Clarke_1866 |
| D_NAD_1927_Definition_1976 | 6608 | Clarke_1866 |
| NAD_1983_(Federal_Base_Network) | 1211 | GRS_1980 |
| NAD_1983_(High_Accuracy_Reference_Network- Corrected) | 1212 | GRS_1980 |
| D_NAD_1983_2011 | 1116 | GRS_1980 |
| D_NAD_1983_CORS96 | 1133 | GRS_1980 |
| North_American_Datum_of_1983_(CSRS96) | 1192 | GRS_1980 |
| North_American_Datum_of_1983_(CSRS)_version_2 | 1193 | GRS_1980 |
| North_American_Datum_of_1983_(CSRS)_version_3 | 1194 | GRS_1980 |
| North_American_Datum_of_1983_(CSRS)_version_4 | 1195 | GRS_1980 |
| North_American_Datum_of_1983_(CSRS)_version_5 | 1196 | GRS_1980 |
| North_American_Datum_of_1983_(CSRS)_version_6 | 1197 | GRS_1980 |
| North_American_Datum_of_1983_(CSRS)_version_7 | 1198 | GRS_1980 |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Anoka | 106700 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Anoka |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Becker | 106701 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Becker |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Beltrami_North | 106702 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Beltrami_North |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Beltrami_South | 106703 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Beltrami_South |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Benton | 106704 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Benton |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Big_Stone | 106705 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Big_Stone |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Blue_Earth | 106706 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Blue_Earth |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Brown | 106707 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Brown |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Carlton | 106708 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Carlton |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Carver | 106709 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Carver |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Cass_North | 106710 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Cass_North |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Cass_South | 106711 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Cass_South |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Chippewa | 106712 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Chippewa |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Chisago | 106713 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Chisago |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Cook_North | 106714 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Cook_North |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Cook_South | 106715 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Cook_South |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Cottonwood | 106716 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Cottonwood |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Crow_Wing | 106717 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Crow_Wing |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Dakota | 106718 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Dakota |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Dodge | 106719 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Dodge |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Douglas | 106720 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Douglas |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Faribault | 106721 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Faribault |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Fillmore | 106722 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Fillmore |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Freeborn | 106723 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Freeborn |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Goodhue | 106724 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Goodhue |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Grant | 106725 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Grant |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Hennepin | 106726 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Hennepin |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Houston | 106727 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Houston |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Isanti | 106728 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Isanti |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Itasca_North | 106729 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Itasca_North |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Itasca_South | 106730 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Itasca_South |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Jackson | 106731 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Jackson |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Kanabec | 106732 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Kanabec |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Kandiyohi | 106733 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Kandiyohi |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Kittson | 106734 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Kittson |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Koochiching | 106735 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Koochiching |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Lac_Qui_Parle | 106736 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Lac_Qui_Parle |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Lake_of_the_Woods _North | 106737 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Lake_of_the_Woods _North |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Lake_of_the_Woods _South | 106738 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Lake_of_the_Woods _South |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Le_Sueur | 106739 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Le_Sueur |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Lincoln | 106740 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Lincoln |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Lyon | 106741 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Lyon |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Mahnomen | 106743 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Mahnomen |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Marshall | 106744 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Marshall |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Martin | 106745 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Martin |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_McLeod | 106742 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_McLeod |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Meeker | 106746 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Meeker |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Morrison | 106747 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Morrison |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Mower | 106748 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Mower |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Murray | 106749 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Murray |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Nicollet | 106750 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Nicollet |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Nobles | 106751 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Nobles |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Norman | 106752 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Norman |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Olmsted | 106753 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Olmsted |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Ottertail | 106754 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Ottertail |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Pennington | 106755 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Pennington |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Pine | 106756 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Pine |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Pipestone | 106757 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Pipestone |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Polk | 106758 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Polk |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Pope | 106759 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Pope |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Ramsey | 106760 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Ramsey |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Red_Lake | 106761 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Red_Lake |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Redwood | 106762 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Redwood |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Renville | 106763 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Renville |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Rice | 106764 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Rice |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Rock | 106765 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Rock |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Roseau | 106766 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Roseau |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Scott | 106770 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Scott |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Sherburne | 106771 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Sherburne |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Sibley | 106772 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Sibley |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Stearns | 106773 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Stearns |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Steele | 106774 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Steele |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Stevens | 106775 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Stevens |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_St_Louis | 106786 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_St_Louis |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_St_Louis_Central | 106768 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_St_Louis_Central |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_St_Louis_North | 106767 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_St_Louis_North |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_St_Louis_South | 106769 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_St_Louis_South |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Swift | 106776 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Swift |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Todd | 106777 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Todd |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Traverse | 106778 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Traverse |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Wabasha | 106779 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Wabasha |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Wadena | 106780 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Wadena |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Waseca | 106781 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Waseca |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Watonwan | 106782 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Watonwan |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Winona | 106783 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Winona |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Wright | 106784 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Wright |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_MN_Yellow_Medicine | 106785 | S_GRS_1980_Adj_MN_Yellow_Medicine |
| D_NAD_1983_HARN_Adj_WI_CP | 106806 | GRS_1980_Adj_WI_CP |
| D_NAD_1983_MA11 | 1118 | GRS_1980 |
| D_NAD_1983_MARP00 | 1221 | GRS_1980 |
| D_NAD_1983_NSRS2007 | 6759 | GRS_1980 |
| D_NAD_1983_PA11 | 1117 | GRS_1980 |
| D_NAD_1983_PACP00 | 1249 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Nahrwan_1934 | 6744 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Nahrwan_1967 | 6270 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Naiad_2000 | 106964 | Naiad_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Nakhl-e_Ghanem | 6693 | WGS_1984 |
| D_Naparima_1955 | 6158 | International_1924 |
| D_Naparima_1972 | 6271 | International_1924 |
| D_NEA74_Noumea | 6644 | International_1924 |
| D_Nepal_Nagarkot | 1111 | Everest_Adjustment_1937 |
| D_Neptune_2000 | 106960 | Neptune_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Nereid_2000 | 106965 | Nereid_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_New_Beijing | 1045 | Krasovsky_1940 |
| D_New_Zealand_1949 | 6272 | International_1924 |
| D_NGN | 6318 | WGS_1984 |
| D_NGO_1948 | 6273 | Bessel_Modified |
| D_Nord_de_Guerre | 6902 | Plessis_1817 |
| D_Nord_Sahara_1959 | 6307 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_North_American_1927 | 6267 | Clarke_1866 |
| D_North_American_1983 | 6269 | GRS_1980 |
| D_North_American_1983_CSRS | 6140 | GRS_1980 |
| D_North_American_1983_HARN | 6152 | GRS_1980 |
| D_North_American_Michigan | 6268 | Clarke_1866_Michigan |
| D_Nouakchott_1965 | 6680 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_NSWC_9Z_2 | 6276 | NWL_9D |
| D_NTF | 6275 | Clarke_1880_IGN |
| D_NWL_9D | 6025 | NWL_9D |
| D_NZGD_2000 | 6167 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Oberon_2000 | 106953 | Oberon_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Observatario | 6129 | Clarke_1866 |
| D_Observatorio_Meteorologico_1939 | 106245 | International_1924 |
| D_Observatorio_Meteorologico_1965 | 106274 | International_1924 |
| D_Ocotepeque_1935 | 1070 | Clarke_1866 |
| D_Old_Hawaiian | 6135 | Clarke_1866 |
| D_Old_Hawaiian_Intl_1924 | 106284 | International_1924 |
| D_Oman | 106206 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| Oman_National_Geodetic_Datum_2014 | 1147 | GRS_1980 |
| Oman_National_Geodetic_Datum_2017 | 1263 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Ophelia_2000 | 106954 | Ophelia_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_OSGB_1936 | 6277 | Airy_1830 |
| D_OSGB_1970_SN | 6278 | Airy_1830 |
| D_OSNI_1952 | 6188 | Airy_1830 |
| D_OS_SN_1980 | 6279 | Airy_1830 |
| D_OSU_86F | 6032 | OSU_86F |
| D_OSU_91A | 6033 | OSU_91A |
| D_Padang_1884 | 6280 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_Palestine_1923 | 6281 | Clarke_1880_Benoit |
| D_Pampa_del_Castillo | 6161 | International_1924 |
| D_Pan_2000 | 106936 | Pan_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Panama-Colon-1911 | 1072 | Clarke_1866 |
| D_Pandora_2000 | 106937 | Pandora_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Papua_New_Guinea_Geodetic_Datum_1994 | 1076 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Parametrop_Zemp_1990 | 6740 | PZ_1990 |
| Parametry_Zemli_1990.02 | 1157 | PZ_1990 |
| Parametry_Zemli_1990.11 | 1158 | PZ_1990 |
| D_Pasiphae_2000 | 106922 | Pasiphae_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_PDO_1993 | 6134 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Peru96 | 1067 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Petrels_1972 | 6636 | International_1924 |
| D_Philippine_Reference_System_1992 | 6683 | Clarke_1866 |
| D_Phobos_2000 | 106907 | Phobos_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Phoebe_2000 | 106938 | Phoebe_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Pico_de_Las_Nieves | 6728 | International_1924 |
| Pico_de_las_Nieves_1968 | 1286 | International_1924 |
| D_Pitcairn_1967 | 6729 | International_1924 |
| D_Pitcairn_2006 | 6763 | WGS_1984 |
| D_Plessis_1817 | 6027 | Plessis_1817 |
| D_Pluto_2000 | 106969 | Pluto_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Pohnpei | 106266 | Clarke_1866 |
| D_Point_58 | 6620 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Pointe_Geologie_Perroud_1950 | 6637 | International_1924 |
| D_Pointe_Noire | 6282 | Clarke_1880_IGN |
| D_Portia_2000 | 106955 | Portia_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Porto_Santo_1936 | 6615 | International_1924 |
| D_Porto_Santo_1995 | 6663 | International_1924 |
| D_POSGAR | 6172 | GRS_1980 |
| D_POSGAR_1994 | 6694 | GRS_1980 |
| D_POSGAR_1998 | 6190 | GRS_1980 |
| D_POSGAR_2007 | 1062 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Potsdam_1983 | 6746 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_Principe | 1046 | International_1924 |
| D_Prometheus_2000 | 106939 | Prometheus_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Proteus_2000 | 106966 | Proteus_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Provisional_S_American_1956 | 6248 | International_1924 |
| D_PTRA08 | 1041 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Puck_2000 | 106956 | Puck_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Puerto_Rico | 6139 | Clarke_1866 |
| D_Pulkovo_1942 | 6284 | Krasovsky_1940 |
| D_Pulkovo_1942_Adj_1958 | 6179 | Krasovsky_1940 |
| D_Pulkovo_1942_Adj_1983 | 6178 | Krasovsky_1940 |
| D_Pulkovo_1995 | 6200 | Krasovsky_1940 |
| D_Qatar | 6285 | International_1924 |
| D_Qatar_1948 | 6286 | Helmert_1906 |
| D_QND_1995 | 6614 | International_1924 |
| D_Qornoq_1927 | 6194 | International_1924 |
| D_Rassadiran | 6153 | International_1924 |
| D_Rauenberg_1983 | 6745 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_Red_Geodesica_de_Canarias_1995 | 1035 | GRS_1980 |
| Reference_System_de_Angola_2013 | 1220 | GRS_1980 |
| D_REGVEN | 6189 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Reseau_Geodesique_de_la_Polynesie_Francaise | 6687 | GRS_1980 |
| Red_Geodesica_Para_Mineria_en_Chile | 1304 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Reseau_Geodesique_de_la_RDC_2005 | 1033 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Reseau_Geodesique_de_Mayotte_2004 | 1036 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Reseau_Geodesique_de_Nouvelle_Caledonie_ 1991-93 | 6749 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Reseau_Geodesique_de_St_Pierre_et_Miquelon_ 2006 | 1038 | GRS_1980 |
| Reseau_Geodesique_de_Wallis_et_Futuna_1996 | 1223 | GRS_1980 |
| Reseau_Geodesique_des_Antilles_Francaises_2009 | 1073 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Reseau_Geodesique_des_Terres_Australes_et_A ntarctiques_Francaises_2007 | 1113 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Rete_Dinamica_Nazionale_2008 | 1132 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Reunion_1947 | 6626 | International_1924 |
| D_Reykjavik_1900 | 6657 | Danish_1876 |
| D_RGF_1993 | 6171 | GRS_1980 |
| D_RGFG_1995 | 6624 | GRS_1980 |
| D_RGNC_1991 | 6645 | International_1924 |
| D_RGR_1992 | 6627 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Rhea_2000 | 106940 | Rhea_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Roma_1940 | 106275 | International_1924 |
| D_Rosalind_2000 | 106957 | Rosalind_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Ross_Sea_Region_Geodetic_Datum_2000 | 6764 | GRS_1980 |
| D_RRAF_1991 | 1047 | GRS_1980 |
| D_RT_1990 | 6124 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_S42_Hungary | 106257 | Krasovsky_1940 |
| D_Sainte_Anne | 6622 | International_1924 |
| D_Saint_Pierre_et_Miquelon_1950 | 6638 | Clarke_1866 |
| D_Samboja | 6125 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_Santo_DOS_1965 | 6730 | International_1924 |
| D_Sao_Braz | 106249 | International_1924 |
| D_Sao_Tome | 1044 | International_1924 |
| D_Sapper_Hill_1943 | 6292 | International_1924 |
| D_Saturn_2000 | 106925 | Saturn_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Schwarzeck | 6293 | Bessel_Namibia |
| D_Scoresbysund_1952 | 6195 | International_1924 |
| D_Segora | 6294 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_Selvagem_Grande_1938 | 6616 | International_1924 |
| D_Serbian_Reference_Network_1998 | 1034 | GRS_1980 |
| Serbian_Spatial_Reference_System_2000 | 1214 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Serindung | 6295 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_SGNP_MARCARIO_SOLIS | 1066 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Sibun_Gorge_1922 | 1071 | Clarke_1858 |
| D_Sierra_Leone_1924 | 6174 | War_Office |
| D_Sierra_Leone_1960 | 106103 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Sierra_Leone_1968 | 6175 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Sinope_2000 | 106923 | Sinope_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_SIRGAS | 6170 | GRS_1980 |
| D_SIRGAS_2000 | 6674 | GRS_1980 |
| D_SIRGAS-Chile | 1254 | GRS_1980 |
| SIRGAS-Chile_realization_2_epoch_2010 | 1243 | GRS_1980 |
| SIRGAS-Chile_realization_3_epoch_2013 | 1252 | GRS_1980 |
| SIRGAS-Chile_realization_4_epoch_2016 | 1253 | GRS_1980 |
| SIRGAS_Continuously_Operating_Network_DGF00P01 | 1227 | GRS_1980 |
| SIRGAS_Continuously_Operating_Network_DGF01 P01 | 1228 | GRS_1980 |
| SIRGAS_Continuously_Operating_Network_DGF01 P02 | 1229 | GRS_1980 |
| SIRGAS_Continuously_Operating_Network_DGF02 P01 | 1230 | GRS_1980 |
| SIRGAS_Continuously_Operating_Network_DGF04 P01 | 1231 | GRS_1980 |
| SIRGAS_Continuously_Operating_Network_DGF05 P01 | 1232 | GRS_1980 |
| SIRGAS_Continuously_Operating_Network_DGF06 P01 | 1233 | GRS_1980 |
| SIRGAS_Continuously_Operating_Network_DGF07 P01 | 1234 | GRS_1980 |
| SIRGAS_Continuously_Operating_Network_DGF08 P01 | 1235 | GRS_1980 |
| SIRGAS_Continuously_Operating_Network_SIR09 P01 | 1236 | GRS_1980 |
| SIRGAS_Continuously_Operating_Network_SIR10 P01 | 1237 | GRS_1980 |
| SIRGAS_Continuously_Operating_Network_SIR11 P01 | 1238 | GRS_1980 |
| SIRGAS_Continuously_Operating_Network_SIR13 P01 | 1239 | GRS_1980 |
| SIRGAS_Continuously_Operating_Network_SIR14 P01 | 1240 | GRS_1980 |
| SIRGAS_Continuously_Operating_Network_SIR15P01 | 1241 | GRS_1980 |
| SIRGAS_Continuously_Operating_Network_SIR17P01 | 1242 | GRS_1980 |
| D_SIRGAS_ES2007.8 | 1069 | GRS_1980 |
| D_SIRGAS-ROU98 | 1068 | WGS_1984 |
| Sistem_Referensi_Geospasial_Indonesia_2013 | 1293 | WGS_1984 |
| D_S_JTSK | 6156 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_S_JTSK_05 | 1052 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_S_JTSK_05_Ferro | 1055 | Bessel_1841 |
| S-JTSK_[JTSK03] | 1201 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_Slovenia_Geodetic_Datum_1996 | 6765 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Solomon_1968 | 6718 | International_1924 |
| D_South_American_1969 | 6618 | GRS_1967_Truncated |
| D_South_American_Datum_1969_96 | 1075 | GRS_1967_Truncated |
| D_South_Asia_Singapore | 106207 | Fischer_Modified |
| D_South_East_Island_1943 | 1138 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_South_Yemen | 6164 | Krasovsky_1940 |
| D_Sphere | 6035 | Sphere |
| D_Sphere_ARC_INFO | 106008 | Sphere_ARC_INFO |
| D_Sphere_Clarke_1866_Authalic | 6052 | Sphere_Clarke_1866_Authalic |
| D_Sphere_EMEP | 106276 | Sphere_EMEP |
| D_Sphere_GRS_1980_Authalic | 6047 | Sphere_GRS_1980_Authalic |
| D_Sphere_GRS_1980_Mean_Radius | 106047 | Sphere_GRS_1980_Mean_Radius |
| D_Sphere_International_1924_Authalic | 6053 | Sphere_International_1924_Authalic |
| D_Sri_Lanka_Datum_1999 | 1053 | Everest_Adjustment_1937 |
| D_ST71_Belep | 6643 | International_1924 |
| D_ST84_Ile_des_Pins | 6642 | International_1924 |
| D_ST87_Ouvea | 6750 | WGS_1984 |
| D_St_George_Island | 6138 | Clarke_1866 |
| St_Helena_Geodetic_Datum_2015 | 1174 | GRS_1980 |
| St_Helena_Tritan | 1173 | WGS_1984 |
| D_St_Kitts_1955 | 6605 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_St_Lawrence_Island | 6136 | Clarke_1866 |
| D_St_Lucia_1955 | 6606 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Stockholm_1938 | 6308 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_St_Paul_Island | 6137 | Clarke_1866 |
| D_Struve_1860 | 6028 | Struve_1860 |
| St._Stephen_(Ferro) | 1189 | Zach_1812 |
| D_St_Vincent_1945 | 6607 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Sudan | 6296 | Clarke_1880_IGN |
| Sun_2015 | 106975 | Sun_2015 |
| D_SVY21 | 6757 | WGS_1984 |
| D_SWEREF99 | 6619 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Swiss_TRF_1995 | 6151 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Tahaa_1954 | 6629 | International_1924 |
| D_Tahiti_1952 | 6628 | International_1924 |
| D_Tahiti_1979 | 6690 | International_1924 |
| D_Tananarive_1925 | 6297 | International_1924 |
| Tapi_Aike | 1257 | International_1924 |
| D_Telesto_2000 | 106941 | Telesto_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Tern_Island_1961 | 6707 | International_1924 |
| D_Tete | 6127 | Clarke_1866 |
| D_Tethys_2000 | 106942 | Tethys_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Thalassa_2000 | 106967 | Thalassa_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Thebe_2000 | 106924 | Thebe_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Timbalai_1948 | 6298 | Everest_Definition_1967 |
| D_Titan_2000 | 106943 | Titan_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Titania_2000 | 106958 | Titania_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_TM65 | 6299 | Airy_Modified |
| D_TM75 | 6300 | Airy_Modified |
| D_Tokyo | 6301 | Bessel_1841 |
| D_Tonga_Geodetic_Datum_2005 | 1095 | GRS_1980 |
| TPEN11_Intermediate_Reference_Frame | 1266 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Trinidad_1903 | 6302 | Clarke_1858 |
| D_Tristan_1968 | 6734 | International_1924 |
| D_Triton_2000 | 106968 | Triton_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Trucial_Coast_1948 | 6303 | Helmert_1906 |
| D_Turkish_National_Reference_Frame | 1057 | GRS_1980 |
| D_TWD_1967 | 1025 | GRS_1967_Truncated |
| D_TWD_1997 | 1026 | GRS_1980 |
| D_Ukraine_2000 | 1077 | Krasovsky_1940 |
| D_Umbriel_2000 | 106959 | Umbriel_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Uranus_2000 | 106944 | Uranus_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Vanua_Levu_1915 | 6748 | Clarke_1880_Intl_Ft |
| D_Venus_1985 | 106901 | Venus_1985_IAU_IAG_COSPAR |
| D_Venus_2000 | 106902 | Venus_2000_IAU_IAG |
| D_Vientiane_1982 | 6676 | Krasovsky_1940 |
| D_Vietnam_2000 | 6756 | WGS_1984 |
| D_Viti_Levu_1912 | 6752 | Clarke_1880_Intl_Ft |
| D_Viti_Levu_1916 | 6731 | Clarke_1880_RGS |
| D_Voirol_1875 | 6304 | Clarke_1880_IGN |
| D_Voirol_1879 | 6671 | Clarke_1880_IGN |
| D_Wake_Eniwetok_1960 | 6732 | Hough_1960 |
| D_Wake_Island_1952 | 6733 | International_1924 |
| D_Walbeck | 106007 | Walbeck |
| D_War_Office | 6029 | War_Office |
| D_WGS_1966 | 6760 | WGS_1966 |
| D_WGS_1972 | 6322 | WGS_1972 |
| D_WGS_1972_BE | 6324 | WGS_1972 |
| D_WGS_1984 | 6326 | WGS_1984 |
| World_Geodetic_System_1984_(G1150) | 1154 | WGS_1984 |
| World_Geodetic_System_1984_(G1674) | 1155 | WGS_1984 |
| World_Geodetic_System_1984_(G1762) | 1156 | WGS_1984 |
| World_Geodetic_System_1984_(G730) | 1152 | WGS_1984 |
| World_Geodetic_System_1984_(G873) | 1153 | WGS_1984 |
| World_Geodetic_System_1984_(Transit) | 1166 | WGS_1984 |
| D_Xian_1980 | 6610 | Xian_1980 |
| D_Xrail84 | 106050 | WGS_1984 |
| D_Yacare | 6309 | International_1924 |
| D_Yemen_NGN_1996 | 6163 | WGS_1984 |
| D_Yoff | 6310 | Clarke_1880_IGN |
| D_Zanderij | 6311 | International_1924 |
Concept Quiz
2.5.2: Horizontal and Vertical Datums
We've explored the idea that the geodetic datum the result of attaching a "free-floating" reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid to a specifically measured geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." via control points and benchmarks. is the product of combining a specific geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." with a selected reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid , starting with the benchmarks Benchmarks are real-world locations which have been carefully surveyed with locations to match a specific geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." . , and establishing all the remaining control points utilizing the principles of labeling intersections with a Cartesian Coordinate System. We noted that the reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid - covered with a grid and with the 2D land and ocean masses drawn upon it - is connected to a geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." - a mathematical derivation of local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features at any point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface via the specific gravitational pull at said point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. , which stores our 3D elevation the vertical distance between local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features and a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface values.
Looking at the creation of the datum in this way makes it seem like there are only "2D datums" and "3D geoids", when in reality, the two work together to produce three kinds of 3D datums: three-dimensional datums. All three come from the initial product: combine a reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid with a geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." via control points (both benchmarks Benchmarks are real-world locations which have been carefully surveyed with locations to match a specific geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." . and mathematically derived intersections) and each serves a specific purpose in Geospatial Sciences. All three are actually a 3 dimensional product, regardless of the fact that only one is called "three dimensional". Everything we have looked at up to this point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. is really a 3D object. Reference ellipsoids, datums, geoids ... all three dimensional objects.
Horizontal datums contain only XY values upon a 3D Earth, vertical datums used to reference locations and distances above mean sea level; elevation. contain only Z values upon a 3D Earth, and three-dimensional datums contain XY and Z values upon a 3D Earth.
Horizontal datums assume that every point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface is at an equal zero elevation the vertical distance between local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features and a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface - including the tops of mountains, the bottoms of oceans, and everything in between. Horizontal datums assume there is no change in topography or relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , and that the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." is totally flat and level at every point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface.
Vertical datums come in three varieties: orthometric datums shows the changes in the Earth's gravitational pull from 0 - any height referenced to the Earth's gravity field can be called as "geopotential heights" which shows the changes in the Earth's gravitational pull from 0 - any height referenced to the Earth's gravity field can be called as "geopotential heights"; tidal datums show the changes in sea level due to tides and are based on local mean sea level which show the changes in sea level due to tides and are based on local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features ; and three-dimensional datums, which combine horizontal datums used to reference location on the Earth's surface, regardless of elevation with ellipsoidal height.
Three-dimensional datums are used by GPS Global Positioning System: A satellite-based navigation system owned and operated by the United States Department of Defense that provides location and time information anywhere on Earth. units to determine a personal elevation the vertical distance between local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features and a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface at any given time. Introduction to GIS Geographic Information Systems the software used to create, store, and manage spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. , analyze spatial problems, and display the data in cartographic layouts Geographic Information Sciences doesn't work with vertical or three-dimensional datums at all, and GPS Global Positioning System: A satellite-based navigation system owned and operated by the United States Department of Defense that provides location and time information anywhere on Earth. for GIS Geographic Information Systems the software used to create, store, and manage spatial data Data that deals with location, such as lists of addresses, the footprint of a building, the boundaries of cities and counties, etc. , analyze spatial problems, and display the data in cartographic layouts Geographic Information Sciences only looks at the fact the if you stand at any given point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface, the elevation the vertical distance between local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features and a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface is known, so for now, just understand that there are a few products of the reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid + geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." process.
Concept Quiz
2.5.3: Geodetic Height and Elevation
Elevation is defined as the measured distance between local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features and the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." . (as we've looked at while examining the geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." creation method, local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features is specified because of the varied effects of the Earth’s gravitational pull; using a global mean sea level the average of the sea level as affected by the pull of gravity when there is a finite amount of water upon a model of the Earth. would create accurate measurements in some places and incorrect measurements in others.)
Altitude is defined as the height of an independent object, such as an aircraft, above ground level (AGL) or Above Sea Level (ASL). If an aircraft was flying at 2,000 feet AGL, it would be 2,000 feet above the ground right below it, no matter the elevation the vertical distance between local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features and a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface of that location. Aircraft can also record values Above Sea Level (ASL), where elevation the vertical distance between local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features and a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface and altitude the height of an independent object, such as an aircraft, above ground level (AGL) are combined. Regardless of how an aircraft is recording measurements, it is not possible for a person to hike to an altitude the height of an independent object, such as an aircraft, above ground level (AGL) , only an elevation the vertical distance between local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features and a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface .
Orthometric height is defined as measured distance between the geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." and the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." . Elevation measurements are created from and stored within vertical datums used to reference locations and distances above mean sea level; elevation. for accurate Z-values within a geographic coordinate system for accurate analysis.
Ellipsoid height is defined as the measured distance between the reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid and the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." . GPS Global Positioning System: A satellite-based navigation system owned and operated by the United States Department of Defense that provides location and time information anywhere on Earth. receivers use ellipsoidal height since the calculation is easier to obtain on the fly. If the GPS Global Positioning System: A satellite-based navigation system owned and operated by the United States Department of Defense that provides location and time information anywhere on Earth. knows where it is in relation to the XY positions on the reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid , it can easily calculate it's height above that established zero. For a GPS Global Positioning System: A satellite-based navigation system owned and operated by the United States Department of Defense that provides location and time information anywhere on Earth. receiver, to calculate elevations based on the geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." is much more labor intensive.
Geoid separation ( geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." height) is defined as the measured difference between the reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid and the geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." . Worldwide, geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." separation varies from +278.87 feet (85 meters) to -351.05 feet (-107 meters), based on the WGS84 reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid and the Earth Gravitational Model 1996 (EGM96) geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." . Geoid separation is used to increase the accuracy of GPS Global Positioning System: A satellite-based navigation system owned and operated by the United States Department of Defense that provides location and time information anywhere on Earth. measurements in the post-processing phase of data collection since the GPS Global Positioning System: A satellite-based navigation system owned and operated by the United States Department of Defense that provides location and time information anywhere on Earth. receiver uses elevation the vertical distance between local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features and a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface established between the reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid and the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." , but accurate measurements are between the geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." and the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." (or the orthometric height the measured distance between the geoid and the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." . ). In order to convert from ellipsoidal height to orthometric height the measured distance between the geoid and the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." . , the geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." separation needs to be a known value. Notice how these height determination definitions can be related back to the kinds of vertical datums used to reference locations and distances above mean sea level; elevation. .
| Figure 2.18: A Graphical Explanation of Ellipsoid Height, Orthometric Height, and Geoid Height |
|---|
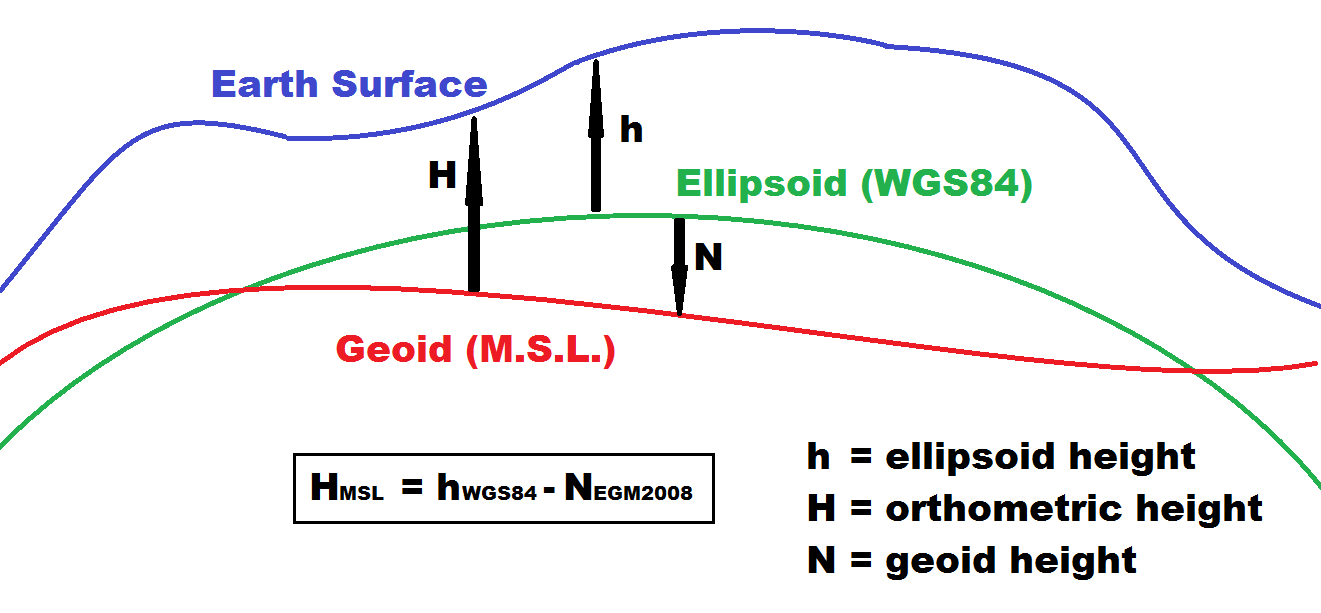 |
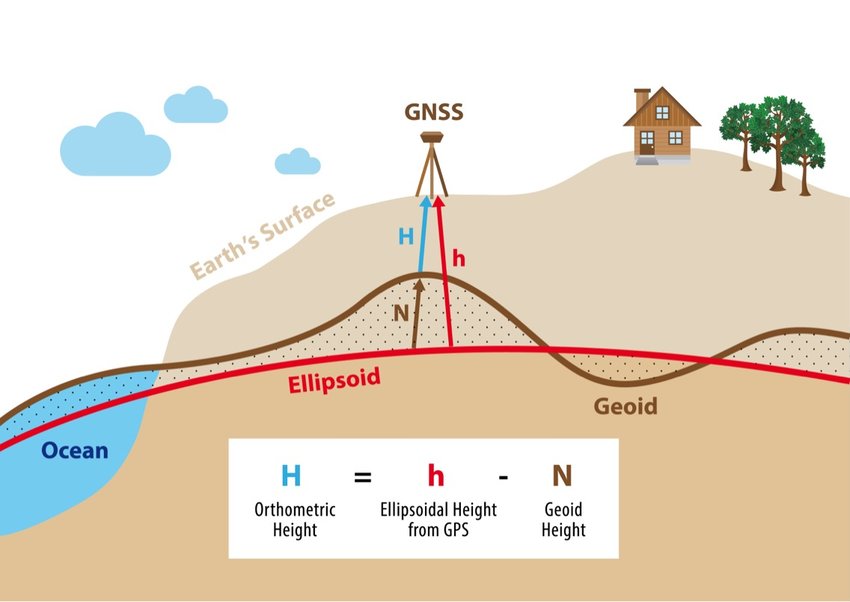 |
| Figure 2.19: Deviation of the Geoid and Reference Ellipsoid in For the World Geodetic Datum, 1984 (WGS84) |
|---|
 |
| This image shows the areas where the reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid and geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." deviate in the WGS84 Geographic Coordinate System. We see that there are really only a few places where the two meet exactly; just the places where the pink and the blue meet in a single line. Most areas of the geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." fall either above or below the surface of the reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid , where the reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid is a smooth, even shape and the geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." is the undulating weirdo shape./td> |
| The Main Point... |
|---|
| Representing the Earth in three ways, geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." , reference ellipsoid an ellipsoid that is drawn to best-fit an area. World reference ellipsoids are drawn to best-fit the entire geoid; local ellipsoids are best fit on one side to a single place of the geoid , and topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." , leads us to a need to know the measured distances between each of them. Each surface serves a different purpose in geodesy the science of measuring and monitoring the size and shape of the Earth and the location of points on its surface , so eliminating one is impossible. |
Concept Quiz
2.5.4: Datum Shifts
Over time, data collection technology improves, while at the same time land and ocean masses are in constant flux - moving, shifting, and boogieing down. As a response to these changes, datum measurements regarding the precision of control points must also be changed to keep up with the shifting world. While it might seem rather obvious, it is a gazillion times easier to move the mathematical points on the datum then to go out, dig up, and physically replace the benchmarks Benchmarks are real-world locations which have been carefully surveyed with locations to match a specific geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." . . And since we know that benchmarks Benchmarks are real-world locations which have been carefully surveyed with locations to match a specific geoid a model of the variation between global mean (average) sea level and local mean sea level the measurement above or below the global average at a single point A GIS vector data in any sort of digital science or art, is simply denoting a type of graphical representation using straight lines to construct the outlines of objects geometry type which is made up of just one vertex pl. vertices One of a set of ordered x,y coordinate pairs that defines the shape of a line or polygon feature. , marking a single XY location in any given geographic or projected coordinate system. on the Earth's surface used for recording the elevation of topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." 's relief the difference between the highest and lowest point within a particular area while landforms are the descriptive words for individual features , which is used to measure precise elevations on the topographic surface a detailed map of the surface features of land. It includes the mountains, hills, creeks, and other bumps and lumps on a particular hunk of earth. The word is a Greek-rooted combo of topos meaning "place" and graphein "to write." . are used for several different datums, moving them to repair the accuracy of one datum would be catastrophic to all of the others.
A datum shift when control points are adjusted via better mathematical calculations or real-world surveying. Benchmarks cannot move, but control points can change via datum shifts. ''Major'' Large effort; many points change; expensive and time-consuming. Noted with a two-digit year (ie NAD83) ''Minor'' Just a few points change. Less expensive; less involved. Noted with a four-digit year (ie. NAD83(1985)) is when the coordinate associated with a benchmark (and the resulting control points) is adjusted or changed based upon either better surveying techniques, better mathematical calculations, or adjustments for continental shift. Datum shifts can be major, noted with a two-digit year following the datum name — i.e. NAD27 to NAD83 — or minor, noted with a four-digit year in parenthesis following the datum name (i.e. WGS84(1988)). Major datum shifts are extremely involved, and usually include a major survey project and mathematical calculations, while minor datum shifts are usually completed when just a few control points are deemed incorrect.
An Example of a Datum Shift
ATLAS OBSCURA: WWW.ATLASOBSCRUA.COM Australia’s Entire GPS Navigation is Off By 5 Feet And now they’re going to fix it. BY JESSIE GUY-RYAN JULY 31, 2016 
If you’re a regular user of satellite navigation services, you’ve likely noticed that the coordinates aren’t always pin-point accurate. If you’re in Australia, you might have noticed a strange consistency in this imprecision — specifically, that everything is about 1.5 meters ( just under 5 feet) off the mark. Now, the Australian government has launched a project to update the datum underpinning its satellite navigation coordinates, compensating for tectonic shifts that have pushed everything on the continent about five feet over from where it’s “supposed” to be. Earth’s landmasses aren’t fixed in place; rather, Earth’s lithosphere (mantle and crust) is made up of numerous tectonic plates, which move over time. This movement explains the separation of Pangaea into the continents that exist today, earthquakes, island formation, and numerous other phenomena. But satellite navigation systems aren’t somehow tracking the movement of Earth’s tectonic plates and updating their maps accordingly. In 2013, George Musser explained how sat-nav really works (and isn’t quite accurate) in a blog post for Scientific American. As he explains it, sat-nav relies on latitude and longitude grids—called datum—just like every other map. But not every system—again, just like maps—relies on the same datum. For example, the United States’ NAVSTAR Global Positioning System (one of only two operational global satellite navigation systems), uses WGS 84, which is tied to the Earth’s core rather than one tectonic plate, but most US. maps use NAD 83, which is tied to the North American tectonic plate. That’s why Google Maps is sometimes a little off, in case you were wondering. As Dru Smith of NGS told Scientific American, the plate-based datum system is basically a compromise to keep surveyors from pulling their hair out. “Most surveyors and mapmakers would be happy to live in a world where the plates don’t move,” Smith explains. “We can’t fix that, but we can fix the datum so that the effect is not felt by the predominant number of users.” As for Australia, it currently relies on the Australia-specific GDA94 datum developed in 1994. Because the eastern part of the Indo-Australian tectonic plate is moving about 5.6 centimeters per year (2.2 inches), the data has become increasingly inaccurate over the past two decades. Five feet isn’t a big deal when you’re getting directions to a nearby town, but as satellite navigation becomes increasingly used in systems that need pinpoint accuracy (think self-driving cars) that little offset becomes a much bigger problem. The increasing need for precision tracking is what motivated Geoscience Australia to establish the AuScope Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) network, which is underpinning the GDA2020 effort that will update Australia’s geocentric datum, bringing it in line with the International Terrestrial Reference Frame used in other regions. The new datum will initially map to where the Australian continent will be located in the year 2020 (hence the name). According to The Register, that means when it first comes into use in 2017, it’ll be about 20 centimeters off. Then, in 2020, phase 2 of the project starts and the project gets really interesting. Phase 2 will synchronize the datum with GNSS, allowing “locations of points and their movement over time to be modeled,” meaning the datum should be continuously up-to-date. So, what about every other country’s sat-nav? We’re all on tectonic plates, and they’re all moving, right? Right—and as we refine our understanding of the planet’s size and shape, our datum will need to be updated too, eventually. In the US., the National Geodetic Survey plans to update NAD 83 in 2022; when that happens, latitude and longitude points in North America will shift at least a meter. “We’re fast approaching the day when people will expect accuracies of centimeters in real time out of their handhold devices and then we’ll see a lot of head scratching as things no longer line up,” Smith told Scientific American three years ago. It looks like that day has arrived. |

